Real Russian cuisine is inconceivable without fish, and first of all - river and lake fish. All the more sad is the reviews of readers who report that in their city it is impossible to buy fresh fish, only frozen, and that on big holidays. In St. Petersburg, fortunately, there is no such problem as a class - Lake Ladoga is nearby, so fresh fish can be bought in any area of \u200b\u200bthe city. I am sure that in other cities this problem can also be solved, if there is a desire.
Maybe there is no demand? But in order for there to be demand, there must be an understanding - what kind of animal this fish is and what it is eaten with, in the most literal sense. So I thought about it and decided to aim at an obviously overwhelming topic, tell everything I know about our Russian fish, and at the same time listen to you, fill in the gaps. You look, together we will raise interest in our national wealth.
In general, any river fish can be boiled in water, broth or steamed, or made into a soup. However, due to their bone structure, some fish are more suitable for certain dishes than others. Understanding what kind of fish is good for what is the first step to letting go of being afraid of it.
Carp
Small (or large) fish with silvery or golden scales. Very tenacious: it became a real discovery for me that if the reservoir dries up, the crucian carp can bury itself in the silt and wait out the dry summer, or survive such a frost in which the reservoir freezes to the bottom. Those who do not like crucian carp usually complain of excessive bony and the smell of mud.
Worth: cheap
How to cook: Dip in flour and fry, or bake in sour cream.

Carp
Reputable fish, veteran of the gastronomic front, especially revered in Eastern Europe. Easily and naturally bred in captivity, gains weight quickly, is inexpensive and sold almost everywhere. I, alas, did not have a good relationship with carp. It would be just bony, this is not so bad, but this specific carp taste ...
Worth: cheap
How to cook: As you wish. Carp is equally well suited for frying, baking, or making soup.

Smelt
A small silver fish is traditionally considered a specialty of the Northern capital: in the spring, St. Petersburg courtyards-wells are covered with the ineradicable smell of fried cucumbers. Meanwhile, smelt is found both in the Russian North and in Far east, and amateur fishermen catch it not only during the spawning period, but all year round. IN last years smelt livestock fell, which was not slow to affect prices. And beware of fakes, under the guise of smelt they often sell something.
Worth: expensive
How to cook: Dip in flour and fry, and when you get bored - dry, marinate or grill.

Bream
Tall, large, stately fish with silvery scales (sometimes with a golden tint). Like other river fish, bream eats away by winter, so late autumn is the time to look for and cook bream. Being a relative of carp, bream has not escaped the common disadvantage of this family - strong boneiness.
Worth: cheap
How to cook: Dry, smoke, fry, bake, including in pies.

Tench
A large, very beautiful fish with small scales covered with a thin layer of mucus, for which the tench got its name. Lin is unpretentious (even more unpretentious than carp), but it can be found on sale not so often. It's a pity: for me, tench is one of the most delicious river fish... Like other fish in this family, tench can smell and taste mud.
Worth: average
How to cook: Fry, bake, boil soup. Line lovers advise not to clean or even wash the fish before frying, because the mucus covering her body turns into a real delicacy. Of course, in this case, it is useful to be sure where this tench was caught.
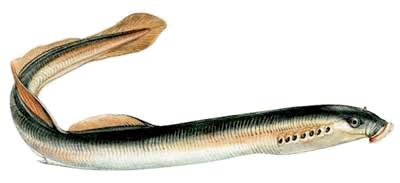
Lamprey
Worth: average
How to cook: Marinate - in this case, lamprey becomes incredibly tasty.

Perch
A spiked river predator, striped like a tiger, and with bright scarlet fins. Perch is not easy to clean - it has hard scales and sharp spines on its dorsal fin. There are quite large ones - about 2 kg. - individuals that, coupled with pleasant taste and the absence of extra bones makes this unpretentious, in general, fish a real delicacy - for those who understand.
Worth: average
How to cook: Smoke, fry, bake, dry. But the main Russian dish of perch is, of course, the ear.

Sturgeon
Not everyone knows, but sturgeons were traditionally called red fish in Russia, meaning not the color, but the excellent taste of this king-fish, which has changed little since the Cretaceous period. Sturgeon is not only black caviar and viziga, but also tender white meat without bones. It is no coincidence that sturgeons were the highlight of the festive Russian table. Now sturgeons are kept in cages in markets and in large stores, so you can buy live fish, being sure of its freshness.
Worth: expensive
How to cook: Bake, cook, grill on coals like a barbecue, cook botvinya, hodgepodge and other soups.

Gudgeon
Small fish with dark specks on the scales. It keeps closer to the sand, for which it received its name. Easy to catch with a line.
Worth: cheap
How to cook: Dip in flour and fry. Small minnows do not even need to be cleaned (but it is better to gut them).

Roach
She's a ram, she's a roach. A silvery fish with red fins and reddish eyes. Like all carp fish, it is rather bony, but very tasty when dried. They write that in Europe roach has practically ceased to be quoted, as edible fish, and most of it is processed into feed and biodiesel. Nightmare.
Worth: cheap
How to cook: Dry, smoke.

Vendace
The vendace looks like a smelt, except that its back is darker. Meanwhile, these two fish belong to completely different orders: vendace is a relative of whitefish and has a similar taste. Vendace is highly prized in Finland, where kalakukko, a traditional rye dough pie, is baked from it. There are very few vendace left in Russian reservoirs, and you can rarely find it on the shelves, but if you see, do not hesitate: vendace is very tasty.
Worth: average
How to cook: Fry, bake (including in pies), smoke, marinate.

Carp
The carp is a wild form of carp, and that says it all. Since carp are bred in large quantities, carp is rarely seen on the counter. But it happens.
Worth: cheap
How to cook: See Carp.
Recipe: See Carp.

Whitefish
The body of the whitefish is elongated, long, covered with silvery scales. As a member of the salmon family, whitefish are renowned for their high palatability, especially when salted and smoked. This fish is also highly valued in Finland and Estonia, where restaurants do not shun whitefish. haute cuisine... One thing is bad: whitefish spoils quickly, and you need to cook it right away, not store it.
Worth: average
How to cook: Fry, salt, pickle, smoke.

Catfish
This mustachioed fish weighs in at several hundredweight, and such large catfish have happened to attack people. Smaller catfish are usually sold on the market, which are good because they are almost completely boneless. Catfish have no scales, but you have to work hard to remove the skin from it - but it gives a great fat.
Worth: average
How to cook: Fry, bake, boil soup.

Zander
As for me, pike perch is the most delicious of all the representatives of the waterfowl of our rivers and lakes. The sweet, tender white meat with little or no bone is worth peeling tough scales and dealing with sharp fins. Usually I try to buy a pike perch with a still meaningful look (as soon as the fish lie down for a bit, and the eyes become transparent), I remove the fillets, and then I cook as I please.
Delicacy fish from ancient times in Russia was considered the main dish on festive table... Moreover, our ancestors called everything especially valuable, beautiful and rare with the concept of "red".
The tradition has been preserved to this day - deliciously cooked fish serves as an adornment for any feast. Red fish is especially appreciated - and this is a variety of representatives of valuable fish species, from expensive to popular. The meat of the red fish is both bright orange or red, and a delicate pinkish color.
It all depends on which family this fish belongs to. In what is still commonly called a red fish. We will now try to figure it out.
Types of red fish
If you follow the division according to trade and culinary characteristics, then three groups of red fish can be distinguished:
- sturgeon;
- salmon;
- white (or pink) salmon.
The first group includes fish that live in the Black, Azov and Caspian Seas, as well as rivers:
- stellate sturgeon,
- bester,
- russian, Siberian, Danube or Amur sturgeon,
- sterlet.
Salmon include fish that live, for example, in the White and Baltic Seas, as well as the Pacific Ocean:
- salmon,
- sim,
- rainbow or river trout and so on.
This fish is so called because of the color of meat and caviar. In addition, the color of the breeding plumage, mainly in males, is bright red.
White salmon include:
- white fish,
- taimen,
- nelma,
- coho salmon and others.
However, other experts fundamentally disagree with this classification and believe that, for example, salmon are not red fish.
In connection with the diverse approach to this topic and the controversy of the issue, we will nevertheless consider all groups of individuals that are usually referred to as red fish.
Sturgeon family
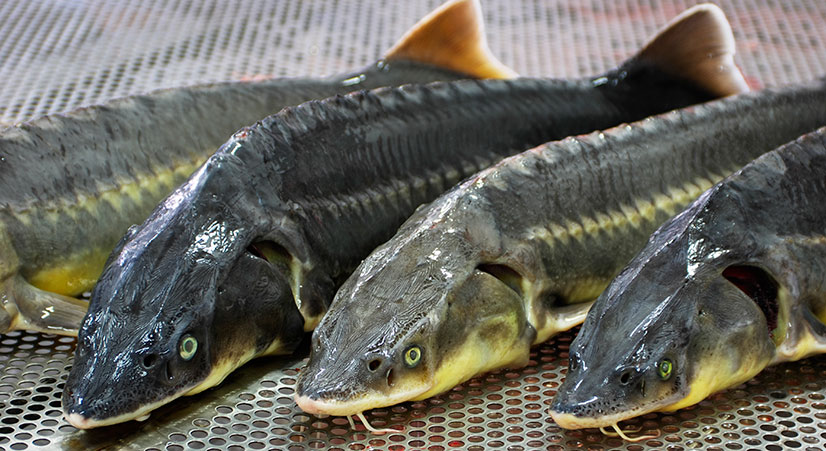

Representatives of this family are one of the oldest fish that appeared in the Cretaceous period - more than 70 million years ago. Such a fish lives in fresh waters and is one of its largest representatives.
Description and habitat
Such fish usually have an elongated body, on the top of the back there are bony shields, and on the head there are bony plates.
Sturgeons keep mainly at the bottom, where they feed on small fish, larvae, worms and mollusks.
All of them (except perhaps the sterlet) are long-livers, but they do not spawn eggs every year, but only once every 2-3 years. To do this, they leave their habitat in the seas and go up the rivers.
Sizes and habits of freshwater fish
The size of freshwater fish also varies greatly. For example, the smallest representatives are such species as high-melting, spike, and fast-growing. They live in streams and rivers, as well as in small bodies of stagnant water. The largest freshwater fish are the well-known catfish and beluga, which are now very rare, as well as the South American arapaima, which grows over four meters in length. Beluga can weigh more than a ton, and there are even photographs of such giant fish preserved in historical documents.
Many freshwater fish are very demanding on the quality and temperature of the water, the presence of currents and natural shelters in the reservoir. For example, pike perch or asp is almost impossible to find in small stagnant water bodies. On the contrary, goldfish, carp and tench are very fond of quiet ponds and lakes with a silted bottom and an abundance of aquatic vegetation.
The most famous species of freshwater fish
Freshwater fish species are divided into families, the most famous and numerous of which is the carp family. Many have seen these fish not only in photos in zoological encyclopedias and reference books, but also live. Typical representatives of carp are such species as crucian carp, carp, bream, carp, roach, silver bream, bleak. Among the representatives of this family there are not only peaceful fish, but also predators, for example, asp.
Other, no less numerous and well-known to fishermen, freshwater fish are representatives of the perch family. The most characteristic freshwater representatives of this group are, as the name suggests, perch, as well as pike perch, bersh, ruff and bass. The appearance of these fish is also easy to recognize by stripes and spots on the body, as well as relatively large eyes. By the way, the name perch just came from the Old Russian word "eye", that is, an eye.
There are only five species of another family of freshwater fish popular among anglers - pike. Among them, common pike, Amur pike and North American maskinong pike are best known for their name and appearance. There is much in common in the appearance of these fish, only the color of the scales differs, and these differences are especially clearly visible when comparing photos of different species from different reservoirs, since different types of pikes are not found in the same reservoir.
Particularly valuable freshwater fish species
Some of the most ancient representatives of freshwater fish are species belonging to the sturgeon family. The names of these fish are also on everyone's lips (sturgeon, sterlet, beluga, kaluga), and even those who have seen sturgeon only in photographs can easily guess their appearance.
.
A characteristic feature of the appearance of these fish is a long nose and outgrowths on the body in the form of thorns. It should be noted that in many reservoirs sturgeon are very small in number or disappearing freshwater species fish, and therefore are listed in the Red Data Books and are under state protection.
Another group of fish, the very name of which excites many sophisticated anglers, is the salmon family. Among them there are both semi-anadromous and freshwater species. The latter include salmon, trout, grayling, lenok, taimen. These fish look very beautiful in the photo, and even catching a salmon representative with amateur tackle will be remembered for a lifetime!
Freshwater stealthy predators
A unique freshwater representative of the cod-like order in the process of evolution turned out to be burbot - a secretive nocturnal predator that prefers cold water, spawns in winter, and spends the summer in hibernation, burrowing into deep burrows closer to cold springs. The appearance of the burbot is easily guessed by the serpentine shape of the body, the spotted camouflage color and the antennae located on the lower jaw.
.
There are three types of catfish in the catfish family. In appearance, these fish are somewhat similar to burbot, but in origin they have nothing in common with this freshwater cold-loving cod. Just like burbots, all catfish are convinced predators by the nature of their diet, and they eat not only fish, but also amphibians, waterfowl and small rodents that swim across the river. The fish are large: for example, the European, or ordinary catfish reaches a weight of 400 kg and grows in length up to five meters.
Other types of freshwater fish
The species of freshwater fish less known to fishermen are representatives of loach, chukuchany, needle, stickleback, goby. Fish from these families can be identified both by name (goby, loach, stickleback) and by photos in ichthyological reference books and zoological atlases.
Record created: 24.11.2015 09:14:01
Fish of our (fresh) reservoirs
Perch
Perch (Perca fluviatilis L.) A very common type of fish, together with the roach it is the most frequently inhabited representative. It is found both in freshwater rivers, lakes and in slightly salted ones. The habitat of the perch is very wide. Perch is found in most of Russia, the Caucasus, the Baltic coast, Europe (except Spain).
By its appearance, the perch is easy to distinguish from other species living in our reservoirs. The body is wide (in large individuals it is noticeably better), there is a kind of hump. The back has a dark green color, the belly is greenish-yellow, 5-9 dark stripes are located across the body. The fins can be bright red to yellow. The eyes are yellow. However, the color can vary and depend on the quality of the water in the reservoir and the habitat (soil).
Perch lives near the bottom, pits, bottom drops, only small perch comes to the shore in summer in search of food. Perch is considered a sedentary fish, therefore it is very stable to catch if you find it. The perch is a very lively, strong, agile fish, if he coveted your bait or found himself on the hook, he will fight to the end. The perch becomes sexually mature in the second year of life. Spawning occurs in March-May, depending on the latitude of the habitat. Usually spawning begins when the water temperature reaches 7-8 *. Unpretentiousness in food helps the perch to survive, but it plays into our hands and it is quite easy to catch it. Perch is caught with a variety of tackles and baits (float rods, donks, spinning rods, rods with a nod, etc.) The unpretentiousness of the fish, a variety of tackles and lures make perch fishing very interesting and simple.
Tench

Tench is a fish of the carp family, has a rounded shape, the body is covered with small scales. The color changes depending on the habitat: from greenish-silver to dark with a bronze tint. Tench is a very beautiful fish. Reaches an average size of 20-40 cm, there are individuals up to 70 cm in size and 7 kg in weight. It is a common representative of rivers and lakes in Europe, and is also found in most regions of Russia. Loves silted areas of the bottom. Tench becomes sexually mature at the age of 3-4 years. Spawning occurs in June-July (in Siberia it can drag on until August), when the water temperature warms up to 18-20 ° C. During the day, the fish practically does not show its activity, only with the onset of dusk and night does it come to life. The ideal time to catch tench is May and the zhor that comes after spawning. As I said, tench is active only at night or early in the morning, an exception may be tench feeding on aquatic vegetation. Lin is well caught on worms, maggots, bloodworms, dough. The most catchy tackle is the float rod. Fishing is quite interesting, but at the same time it is difficult and unpredictable.
Carp

Crucian carp is a truly ubiquitous fish and perhaps everyone caught it, so everything new is well forgotten old. In total, there are two types of crucian carp in nature: golden - the body is rounded, golden-colored scales, lives in stagnant water and silver - the body is more flattened, silver-colored scales, lives in lakes and rivers. Crucian carp lives in the lakes of eastern Europe, the central zone of Russia, Siberia. The mass of an adult is usually within the range of 500-800g. However, there are cases of catching individuals weighing up to 3 kg. Crucian carp fish is unpretentious to habitat conditions, external weather factors. Spawning in warmer latitudes occurs in May, in colder latitudes in June.
Crucian carps spawn at a temperature of 15 degrees. They live near aquatic vegetation. Large individuals stay away from the coast, approaching only early in the morning. When do we catch? The pre-spawning period is considered the best period (determined by the temperature of the reservoir). Throughout the year, crucian carp is caught unevenly, the bite depends on the weather and many factors. The best bite is celebrated at dawn and at evening hours... What are we catching on? In the summer-autumn period, dung worms and bread crumb sprinkled with anise oil will help us out. As a bait, you can use a ready-made store or cook it yourself. Tackle. Ordinary telescopic rods work well. Line - 0.2, lead - 0.1-0.15. The rest is selected according to the fishing condition. In conclusion, I want to say that it is interesting to catch crucian carp because of its good resistance, it is widespread and not picky. All this provides us with an interesting and exciting fishing!

One of the largest and most voracious predatory fish in our reservoirs is the catfish. Catfish is a large fish of the catfish family. The body is scaleless. The catfish's appetite is simply wonderful, it eats a variety of fish, frogs, molluscs, crustaceans and even waterfowl.
In addition to its appetite, the catfish can boast of its size, so the champions reached 5m in length and 300kg in weight. By its shape, the body of the catfish is adapted to the bottom lifestyle. The color in most cases is black-brown, brown or gray with sandy shades. The color depends on the habitat of the fish. The head is large, and there are many teeth in the huge mouth. The upper jaw has two long antennae, and the lower one has four. The anal fin is long and flows smoothly into the caudal.
It inhabits the territory of most of Europe (except for the western and northwestern parts), as well as the territory of Russia. Leads a nocturnal lifestyle. Almost all the time he is in pits, whirlpools and only goes hunting at night. Sometimes you can see him in shallow water or backwaters. The best fishing period is the end of spawning. In July-August, when the water warms up to a temperature of 18-22 degrees, the catfish begins to spawn. With the onset of evening and before dawn, the chances of catching our giant are quite high.
To catch catfish, we need a sufficient amount of bait. Frogs, worms, and snail meat have shown themselves well. A proven method of catching catfish over the years is catching on a donk using a "kwok". Quite an interesting and exciting way to fish. Catfish is a lively, strong fish that brings a lot of fun to catch.

Ide is a very beautiful fish. The entire body is shimmery with a golden color, and the fins can be from red to gray. Ide has a fairly wide body. An adult ide usually weighs 2-3 kg, but can grow up to 6 kg. The ide has a small mouth. The ide is not considered a predatory fish, however, after reaching a weight of more than 0.4 kg, it actively feeds on small fish.
Ide lives in most of Europe and Russia. Loves middle-flow rivers and stagnant water bodies. Spawning occurs in April-May at a temperature of 12-15 degrees. Loves rifts, thickets and driftwood, changes in the bottom topography.
Ide is best caught immediately after spawning. At this time, it is great to go fishing early in the morning or closer to lunch. You should take with you maggots, May beetles, worms, corn, wheat. Of the tackle, they prefer a float rod, bottom tackle, spinning and fly fishing tackle. My favorite fishing method is a spinning tackle equipped with small spinners in a bright silver color. We read how to choose a spoon for fishing in my article. With this method of fishing, you will get the most out of the resistance of the ide on your hook.
Asp

Asp is a predator of the carp family. It has a long body with a large mouth. The sides are silvery, the back is dark gray. The dorsal and caudal fins are gray, while the lower and lateral fins are orange-red. The scales are small.
Asp lives in most small and large rivers flowing into the Black, Azov, Caspian and Baltic seas. It is also found in the territory of Central Asia.
The asp reaches puberty at a weight of 0.5kg and four years of age. Spawning occurs at a water temperature of at least 6 degrees. Loves rocky bottom, rifts. It is best to catch the asp after spawning, during this period it is actively fattening up. Morning time is good for catching asp, because at this moment it is at its maximum activity.
What to catch asp? We use fly fishing and spinning. When fishing with a spinning rod, use small lures (due to the anatomical structure of the mouth and the absence of teeth, the asp cannot hunt large fish). Light-colored spinners and spoons have proven themselves well.
Carp

Carp is a domesticated form of carp. Very popular in terms of breeding. So, the great interest in this fish led to the emergence of "breeds". They differ in body shape and the amount of scales. In golden carp, the scales are dense and have an average size, in mirror and king carp, it is small and very large, in frame carp it is absent.
The secret to the popularity of carp. The main secret of economic popularity is its growth rate, omnivorousness, not fastidious about its habitat. Anglers love the carp for its size, preparation and fishing process, and undoubtedly for its resistance when playing.
The color of carp scales is from yellow-green to brown, the body is thick, the scales are large. The back is darker in color, the belly is lighter. The color can vary from the habitat of the carp. The head is large. The lips of the carp are well developed, on the upper lip there are two pairs of short whiskers. The dorsal fin is long, the rest are short.
Carp lives in reservoirs, lakes, rates, rivers, artificial pits. Prefers stagnant or slow flowing water with a muddy or clay bottom. May be found in slightly salted waters. During the day it goes deep, at night it swims into shallow water. Spawning occurs at a water temperature of 10 ° C. For spawning, carp chooses small areas of the reservoir with abundant vegetation.
They begin to catch carp immediately after spawning at a water temperature of more than 10 ° C and until September, rarely October. Carp feeds on both plant and animal food. The diet of carp includes: worms, molluscs, small crustaceans, larvae, etc. Well suited for fishing: dung worm, dough, maggot, pearl barley, peas, corn. An important element and the key to success is carp bait. A properly prepared groundbait will not leave you without fish. It is rational to use flavors and attractants, which I already wrote about earlier. Feeder and float gear, bottom gear are well suited for fishing.
Pike

The pike is the most insatiable robber of most bodies of water. It is difficult to confuse a pike with another species. The body has an elongated shape, the sides are slightly flattened, a wedge-shaped head with a huge mouth and many teeth. The body has a spotted or striped color, the back is dark green, the belly is light. The color depends on the habitat, so the pike living in snags of a darker color. River pike, in comparison with lake pike, has a longer body. Likes to wait for fish near aquatic vegetation, snags, whirlpools. The pike is a lone predator. It grows quickly, with normal nutrition it reaches a weight of 1 kg after three years.
When to catch pike? There are three main zhora: the first (immediately after the ice melted), the second (a week after spawning), and the third (in the fall in September-October). However, the pike bite both in summer and winter, but the bite is weaker.
What to catch pike with? Zywiec - the best choice... Artificial baits are also good for use. It often happens that a pike attacks your bait with bread, maggot or pearl barley when fishing with a float rod. Or even attacks the caught fish on your hook while playing.
Chub

The chub lives in rivers and lakes with running water. The body is oblong, cylindrical, head with a wide forehead. The back is dark green or grayish, the sides are silvery with a pink tint. The fins are orange except for the dorsal fins. The chub becomes sexually mature at four years old. Spawning occurs in May at a water temperature of 14 degrees.
In clear weather, the chub prefers to stay on the surface, hunting fish and insects that have fallen into the water. It can also hold on to deeper places of the reservoir, but it must float up for food. Spring and summer are considered the best times of the year for chub fishing.
Chub is caught both on baits of animal origin (worm, maggot, frogs) and artificial baits. You can catch a chub on fly fishing, bottom tackle, spinning. Chub is a very beautiful fish. Catching a chub is a pleasure.
Zander

Pike perch (Lucioperca lucioperca (L.)). Perhaps everyone recognizes the appearance of pike perch. Its elongated body and head remind us a little of a pike, but from it it also took its predatory disposition. Along the back, the pike perch has a dark greenish-gray color, the belly is light in color, and gray spots are found throughout the body. Pike perch is found in the basins of the Black, Azov, Caspian Sea, Eastern Europe, however, it is found in the Baltic States and Siberia.
Pike perch usually stands still (sedentary). It stays near a rocky bottom, pits, sunken logs, likes changes in depths. Only young bastards come to the shore. Pike perch is a very voracious fish, watching its hunt, you can see how it jumps out of the water or drives flocks of fish to the very shore.
Zander spawning begins from the end of March (Volga) to May. Spring is considered the best time of the year to fish for walleye. As for catching pike perch, live fish show good catchability in ponds or places with deep holes. It is also very interesting to fish for pike perch on spinning. Wobblers and spinners work well.
Guster

Today we will talk about such a wonderful fish as silver bream. The body of the silver bream is high, strongly compressed on the sides, covered with dense medium-sized scales. The head is small with a small retractable mouth and large eyes. The back has a gray-blue tint, the sides and abdomen are silvery. The dorsal fin is gray, while the anal, caudal, and pelvic fins can be yellow to pink or reddish in color. It is the color of the fins and larger scales that can be distinguished from a thicket that is very similar to it.
bream.
Guster lives in a wide range in most rivers, lakes and ponds in Europe. Gustera prefers places with a weak current and a sandy or clayey bottom. All large individuals stay at depth. Only with a decrease in water temperature does the whole silver bream go to winter.
Spawning occurs in May-June. The diet of silver bream includes: algae, molluscs, crustaceans, worms, larvae.
Among the fishing methods, I would like to highlight float and feeder gear.

Ruff is a fish of the perch family. Widely distributed in Europe and northern Asia. Found in the USA.
The body of an adult does not exceed 10-15 cm in length. The weight of an adult is 10-25 grams. The back is gray-green, the abdomen is light. The fins are dotted with black dots. As a rule, the color of the ruff depends on the living conditions.
Ruff is a rather unpretentious fish and can inhabit rivers, lakes, ponds, canals, slightly salted reservoirs. Spawning in ruffs can take place at a water temperature of 6 to 18 degrees.
It prefers to swim near aquatic vegetation, a sandy bottom, where it can be found in fairly large flocks. Ruff feeds on small crustaceans, worms, leeches. However, more often it itself becomes food for predators. Ruffs are great as live baits.
Loach

Loach is an exotic local fish. This is how I would like to characterize it. The body of the loach is thin, laterally flattened and elongated, the head is extended forward, the mouth is lowered down and surrounded by ten antennae. The fins are small, the posterior is rounded, the scales are small. The color of the loach can be quite varied: from black to light green or sandy. The back is dark, dotted with spots, along the entire body there are about four stripes of different widths and shades, and the abdomen is light or yellowish.
The loach is rightfully considered one of the most unpretentious fish to living conditions. So, the loach can breathe not only with the help of the gills, but also with the help of the stomach and skin. It is because of the peculiarity of breathing through the stomach that we can hear the characteristic squeak of loaches. He can live in the most silted reservoirs, and is also not afraid of the drying out of the pond. In such cases, the loach burrows into the silt and hibernates.
Widely distributed throughout Europe. The loach keeps at the bottom of the reservoir. During the day, its activity is minimal, and with the onset of dusk, it becomes more active. Usually loaches keep in small flocks. Spawning occurs in May-June at a water temperature of 16-18 degrees. They grow fairly quickly and reach sexual maturity at the age of two.
The loach feeds on small molluscs, crustaceans, and worms. Anglers often use it as live bait for pike.
Ukleya (verkhovodka)

Ukelea is a very common fish of the carp family. Distributed almost throughout the territory of Ukraine and the European part of Russia. This type has no industrial value. Considering bleak, I focus not on the quality of the catch, but on the interest in catching this type of fish. So, most professional fishermen hone their skills on catching this fish.
The body of the bleak is elongated and strongly flattened. The scales are small, the back is dark green in color, and the sides and abdomen are silvery. The fins are dark or yellowish. The eyes are large. The mouth is directed upwards. The average length of the bleak is 10-15cm, sometimes the length reaches 20cm. Usually, the weight of an adult does not exceed 50g.
Bleak has a gregarious lifestyle. And lives in rivers, lakes, reservoirs. Prefers the upper layers of water with a moderate current. It prefers to swim in open areas, in summer it floats on the surface of the water. It feeds on plankton and small larvae that have fallen into the water.
I think the best fishing tackle is a float rod. There are no special requirements for it. We use gear without an extra margin of safety - we don't need it.
Bleak likes to see maggots, worms, dough as bait. Groundbait should be used in moderation. The main thing is to attract the attention of the flock of bleak. Our groundbait should be mixed with sand or earth. In most cases, no groundbait is needed.
The caught fish can be salted on a ram or used as live bait.

Bream is a representative of freshwater waters and belongs to the carp family. The scales are small enough and have a silvery color. On the abdomen it can be almost white, and on the back with a gray tint. Like many other fish, the color of the scales depends on the habitat of the fish and the water of the reservoir, so the color of the scales of a bream can be slightly golden or greenish. Adults can reach a weight of 10 kg, but this is rare, average individuals weigh about 2-3 kg and have a length of 40-50 cm.
Bream lives in reservoirs with running and stagnant water. In rivers, he chooses areas with a small current and quiet backwaters. In such places, he and feed, preferring small crustaceans, molluscs, worms, larvae, aquatic vegetation. Spawning occurs with water warming at the end of April.
Bream is a rather cautious fish. Most often it can be seen in flocks. During the day, he is in deep holes or places with abundant aquatic vegetation. At night it goes out for intensive feeding. If you are going to fish for bream, then as bait you should use mixtures that form a cloud at the bottom and will attract fish. Bream prefers natural ingredients in groundbait and natural aromas. In my opinion, cooked porridge made from various types of cereals will be an excellent substitute for purchased groundbait. In addition, you can cook semolina with peas. Bream loves pearl barley, peas, worms, maggots, dough, corn as bait.
Considering tackle for catching bream, I would like to highlight float tackle, nod fishing rod, donk.
Roach

Most likely it is this fish that is most often on your hook. Roach is found in most rivers, lakes, and reservoirs. The caution of this fish does not prevent us from catching it and enjoying it.
Roach belongs to the carp family. The body is elongated, the scales are bright silvery. The back can be dark green to black. The eyes are orange. The fins are orange or red.
Such distribution of roach in various reservoirs is due to its unpretentiousness to food. Roach can eat plant and animal feed. The growth rate of roach depends on the amount of food in the reservoir. I would like to note that roach grows very slowly, so by the age of 5 its weight reaches about 100g. However, the record holders weighed more than 1.5 kg, which means there is still a chance to catch a trophy roach.
The roach becomes sexually mature at the age of 3-5 years. Spawning occurs in April-May at a water temperature of 10-12 degrees. The best bite happens before and after spawning in May and June. To find roach in a pond, you should know its favorite habitats. Roach loves to flock near aquatic vegetation, loves a sandy bottom (often roach go out to feed on beaches with a sandy bottom, in the morning there is a good bite in such places), keeps near pitfalls, logs.
Roach does not pick up food. The worm, bloodworm, maggot, dough, pearl barley show themselves excellently.
To catch a roach we need a float rod. A reel can be attached to the rod to make it more versatile. We take a thin line 0.1-0.15mm. We select the right size hooks. The float must be sensitive.
When fishing for roach, the main thing is to always be ready to do a good sweep.
Rudd
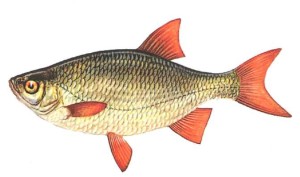
The rudd is one of the most beautiful freshwater fish. In appearance, it resembles a roach. The body of the rudd is high, the back has a gray-green color, the sides are silvery. The fins are bright red. The eyes are orange with a red dot at the top. Comparing rudd with roach, I would like to note that in rudd, unlike roach, the corners of the mouth are directed upwards, and the dorsal fin is also displaced to the tail. The belly of the rudd is more compressed.
The presence of a rudd in a reservoir is an excellent indicator of its purity. Rudd loves unpolluted rivers and lakes. Fry swim along the coastline in schools. Larger individuals prefer thickets of vegetation and reeds. It is in the gaps of aquatic vegetation that you should catch it.
Rudd spawns when the water temperature reaches 18-20 degrees. The rudd starts spawning at the age of 5 years and a body length of 13cm. Adults can reach a weight of 0.5-1kg and be over 35cm in length.
It should be noted that the rudd eats actively only during daylight hours. I noted spring and summer as the best biting period.
They catch rudd with a wide variety of baits. A worm, maggot, bloodworm, dough, pearl barley are perfect. Sometimes there are cases of catching a rudd for 1-2 grams of a spinner and a spinner for spinning tackle. The best tackle for catching rudd is a float rod. You can also use fly fishing gear.
Gudgeon

Gudgeon is a schooling fish, the size of gudgeon is very small, it reaches a weight of 50 - 150 grams. The appearance of the gudgeon is adapted to its habitat, and in the gudgeon it, in turn, is bottom and sandy. The back of the gudgeon has a slightly darkish color with shades of yellow. The rest of the fish's body is silvery. The gudgeon's eyes are yellow, and the fins are gray. The gudgeon lives throughout Europe and Russia, the only exceptions are the extreme northern latitudes. Gudgeon lives both in lakes and rivers. But a large number of it lives in the rivers, it is there that the largest specimens live.
The gudgeon spends his whole life in shallow waters, he is looking for a sandy, clay or rocky bottom. There he also finds food for himself, since the gudgeon is a bottom fish, the main food in his diet will be insect larvae, worms, molluscs, small crustaceans. Gudgeon leads only a daytime lifestyle, so you can catch it only during the daytime. Early morning and sunset are best for this. It is caught all year round, but the best periods for fishing are summer and early autumn.
Gudgeon spawns from early April to late May, during this period the gudgeon lays eggs on stones, grass, driftwood. Most of it does not survive, as it becomes food for the rest of the fish and the gudgeon itself. The best tackle for gudgeon fishing is a float rod, with which you can catch it. Maggot, worm, dough are perfect for bait. But counting on a solid catch is not worth it. Gudgeon is a small fish and is caught only for the sake of entertainment, and often it comes across completely by accident.
Grayling

Fish of the grayling family, like the salmon family, have an adipose fin, and therefore they are often confused, but they differ from salmonids with a large and high dorsal fin. The family of grayling is represented on the territory of Ukraine by only one species - grayling. On the territory of Russia, you can find its subspecies. The body of the grayling is elongated and rather thin, covered with medium-sized scales, the fins are small, the only exception is dorsal. The color of the body itself changes with age and season. The back is usually gray with a shade of green, dotted with black spots. The abdomen is silvery white. The fins are yellow.
Grayling is a fish of fast-flowing rivers. He is very picky about the presence of a large amount of oxygen in the water and the purity of the water itself. All these factors indicate to us that grayling can be found in places with fast currents and running water, rocky bottom with depth differences and the presence of holes are favorite habitats.
Grayling is sedentary. The exception is young individuals huddled in flocks of up to 10 individuals. The grayling leaves its habitat only at night. He even hunts near his home. The attack takes place on passing fish.
Puberty in grayling begins at the age of three, until this moment it is actively growing. Spawning occurs in the upper reaches of the rivers, it is upstream that the grayling is sent for spawning. The main food of grayling is small fish, insects, worms, crustaceans, caviar of other fish species. Summing up, we can say that grayling lives in mountain rivers with a fast current. They catch grayling on spinning rods using special wobblers or bait imitating insects.
Carp

The carp is a rather large fish, it can weigh up to 20 kg, so anglers like it very much. It is found in the middle latitudes of Russia, throughout Ukraine. Inhabits lakes and reservoirs. Outwardly, the fish looks very strong, therefore, when playing, it creates a lot of resistance, is covered with large golden scales. Spawns at a water temperature of 17-22 *. After spawning, in 1-2 weeks the carp begins to actively bite. It is worth fishing near reeds and aquatic vegetation. The tackle should be very strong, line within 0.2 - 0.5 mm and hooks 8-12 sizes. But far from all anglers have ever caught a carp, and if he did come across, then in most cases these are individuals weighing from 1 to 3 kg. The carp habitat is the basins of the Black, Azov and Caspian Seas. It can also be found in reservoirs throughout Russia, but this is due to the artificial launch of fish into the reservoir.
Carp is a freshwater fish, it eats aquatic vegetation, worms, snails. The food is quite diverse and includes both plant components and animal origin. The carp is very voracious and grows very quickly, it is also omnivorous, so it is artificially launched into reservoirs for purification. Carp is a thermophilic fish, therefore spawning occurs at a temperature of 17-22 *, the fish lays eggs in small bays, after which the main zhor begins which lasts for 2 weeks, the best temperature for catching carp is 22-30 *. It is very difficult for beginners who do not know the habits of a carp to find and catch it. The carp keeps close to pits with uneven bottom topography and depth differences. You can find a carp simply by looking closely at the water surface, in the morning the carp goes in search of food and very often swims to the very surface of the water, creating characteristic splashes.
In different places, carp is caught in different ways. The main methods of fishing are a float rod and a rubber band. When fishing with a line, you need to take a long and strong fishing rod with a strong fishing line and a large hook, the float and the weight depend on the specific place of fishing. When fishing with an elastic band, a strong tackle is also used. Fishing with an elastic band has its advantages, it can be caught at night, it will be very difficult to see the float with a fishing rod, given that the bottom fish loves depth and lives far from the shore, the elastic has its advantages in this regard.
Worms, cake, snails are used as bait. The carp takes the bait very carefully. Often, a lot of time can pass before the bite is confident, the carp looks closely and tastes it. Given that the carp's bite is very unstable and changeable, it becomes very difficult to catch this fish.
Rotan

Rotan is a fish of the Golovyoshkov family. Its appearance is fully consistent with the name of the family. The head of a rotan occupies a third of the entire body, the mouth of the fish is large and equipped with small teeth in several rows. Rotan lives throughout Asia, mainly in the northern part, as well as in eastern Europe. Body color varies by habitat and can range from black to lighter shades. Inhabits rivers and lakes. Its main habitat is rivers, in which its size reaches the maximum possible. Reaches a size of 25 cm and a weight of 350 - 400 g.
Rotan is a predatory fish that feeds on worms, larvae, crustaceans and small fish. Compared to other predatory fish, it behaves less actively and is in many ways inferior to its neighbors - perch and pike. Therefore, it feeds not only on fish but also on other animals and even vegetation. Spawning occurs between March and April. Rotan is caught on a float rod by casting the bait near vegetation or the border of vegetation and clear water. The tackle is not used powerful, since the rotan is not a large fish, the hook will fit 5-8 sizes, and the fishing line with a diameter of 0.15-0.2 mm. As with other predatory fish, it is worth using a leash, but this is not required.
Rotan's bites are rather sluggish, so it is difficult to catch it, you need to have good exposure and be able to pause before striking. Worms, bloodworms, maggots, small fish will fit into the bait. Rotana is interesting to catch, but you should not count on a solid catch. You can count on a big catch only on rivers rich in rotan. In other cases, he comes across by pure chance.
Chekhon
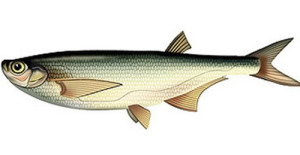
Chekhon is a fish living in lakes and rivers of Eastern Europe, as well as central Russia. Chekhon can be found both in stagnant water and in rivers with the current. It lives at a sufficient depth, so fishing from the shore is problematic. He tries to stay close to snags, stones, vegetation. All these factors make fishing for sabrefish very difficult, for you such fishing can result in the loss of tackle that you hook onto driftwood, and playing fish in such conditions becomes a difficult test for a fisherman's skills.
This type of fish spawns from April to May. During this period of the year, the fish bite well and have a decent weight. It feeds on sabrefish on small animals living in the reservoir: larvae, worms, small crustaceans. It is better to catch sabrefish in the summer, early in the morning or at sunset. It is better to catch sabrefish in the summer early in the morning or at sunset. They catch sabrefish in most cases with float rods. Maggot, dung worm is perfect for bait. Your tackle should be of medium strength, although the weight of the saberfish does not exceed 0.5 kg, but it actively resists. But this is more of a formality, since some anglers still use old-fashioned methods and catch it from a boat using only a fishing line and a hook.
Chekhon is caught from early spring to late autumn. In summer, sabrefish can live and feed in the upper layers of the reservoir. In winter, sabrefish is generally not caught, since it does not bite actively. But if you decide to go for winter fishing on sabrefish, the float rod will help you with this. Chekhon is appreciated for its taste, the best is considered to be the saber caught in spring and autumn, it is fatty and the ram from it turns out to be very tasty.
Burbot

Burbot is a fish that can compete with catfish in its extravagant appearance. The body is cylindrical from head to tail. The dorsal fin is very long and reaches the tail. The anal fin is also long. The caudal fin is rounded. The back has a dark green spotted color. The rest of the body is dark in color.
Burbot is a lover of northern cold rivers, therefore, it loves deep pits with oxygenated water. Spends all his life in pits and is nocturnal. He hunts only at night, his developed sense of smell and hearing helps him find prey. Spawns in winter, usually in February. Sexual maturity begins at 4 years of age. Spawning occurs at a water temperature of 0 *. The laid eggs ripen until spring.
Young burbot feeds on mollusks, crustaceans, worms. Larger individuals feed on young fish, crustaceans. The burbot eats most actively from April to May at this time, it goes to the coastline and hunts for spawning fish, as well as their eggs; in summer, it rolls into pits and eats less actively. In late autumn, burbot is actively feeding again, gaining weight for wintering.
The largest number is found in the rivers flowing into the Arctic Ocean, but it can be seen in the rivers flowing into the Black, Azov, Caspian seas. The most interesting thing is that burbot is found only in rivers with perfectly clean water.
Burbot is caught mainly in winter on girders and a jig. Burbot is considered very delicious fish and therefore very much appreciated by fishermen. Catching a burbot is considered a great success.
Dace

Yelets is one of the most common fish in Russia. The dace is second only to roach in number. Eltsy live in rivers and lakes with always clean water. They live near the sandy bottom, looking for natural shelters. Reeds or algae can serve as such shelters. The body of the dace is flattened on the sides, the back is painted black, the abdomen is painted silver. The fins are yellowish.
Dace is a small fish, its maximum length is 25-30 cm and reaches 500 grams. Spawning takes place from March to April, if the water is not warmed up enough, it can drag on until the end of April, the beginning of May. Dace is a bottom fish that lives in backwaters with a small current. But it often rises to the upper layers of water to feed on small insects. Dace feeds on bloodworms, worms, small crustaceans, grass. This diet is due to the fact that the fish is bottom.
The best period for catching it will be summer, or rather the daytime period of the day. It is best to catch dace with a float rod. Also, very often, a wiring technique is used to catch it. The tackle should be light and comfortable, a hook of 3-5 sizes, as well as a line of 0.15-0.2 mm, will do. As bait can be used from bloodworms and dungworms to artificial flies and grasshoppers. Biting is best in late summer and autumn. During this period, dace is actively fattened for the winter, you can catch it near the shore, while the size of the fish you may come across is completely different. In winter, it is very difficult to catch him because he rolls into pits and eats little actively. Dace is a common fish on the territory of Russia, it is easy to catch, and the bite is stable.
Tench - carp fish , the only representative of the genusTinca. The short, tall and thick body of the tench is covered with small, tight-fitting scales and a thick layer of mucus. The color of the body depends on the living conditions: from greenish-silver (in transparent water with sandy soil) to dark brown with a bronze tint (in reservoirs with silty soil). The dorsal and anal fins are relatively short. Caudal fin without notch. In the corners of the mouth, there is one short (about 2 mm) antennae. Branchial stamens 14-20. The eyes are small, red-orange in color.The tench is 20-40 cm long, can reach 70 cm and weigh up to 7.5 kilograms. Lin got its name for its ability to change body color in the air.
By means of artificial selection, a decorative form - a golden tench - was bred. It has an intense golden color and dark eyes.
The tench becomes sexually mature at the age of 3-4 years. Tench is a thermophilic fish, therefore it begins to spawn in June-July at a water temperature of 18–20 ° C. Spawns in macrophyte thickets.

Common catfish-
large freshwater fishless fish of the catfish family of the order catfish. Body length up to 3 m, weight up to 150 kg.The anal fin is long, the adipose fin is absent, and the unpaired fins have no spines.The color in most cases is brown with shades of brown-green, the belly is white. Depending on the habitat, the color can vary from almost black to light yellow. Sometimes, very rarely, albino catfish are found.Inhabits rivers and lakes of the European part of Russia, except for the Arctic Ocean basin. Common in Europe and the Aral Sea basin
Spawning in the spring in the coastal zone among aquatic vegetation. The female lays eggs in the nest, which the male guards. Sexual maturity occurs, usually in the fifth year of life.
There is a misconception that catfish feeds only on carrion and spoiled foods. In fact this is not true. The main food of catfish on early stage development are small crustaceans, fry and aquatic insects. At a more mature age, depending on the food base, he prefers live fish and other freshwater animals and mollusks in his diet. There are also known cases of attacks on waterfowl and small domestic animals.
An active nocturnal predator. During the day he prefers to lie down in pits, in a snag and under kupak. In many regions, the common method of catching catfish with a kwok.
Before freezing, it gathers in pits in small groups of 5 to 10 individuals. In winter, it does not feed and is practically inactive.

River perch - fish of the genus perch family perch family
, a detachment of perchiformes.River perch is a predatory fish: other freshwater fish occupy a significant share in the diet of adult perch.... River perch prefers to stick to flat water bodies, it can be found in rivers, lakes, ponds, reservoirs, and even in less brackish areas of the seas. The spawning of the river perch takes place in early spring, the female perch lays eggs in the form of a long (up to 1 m) gelatinous ribbon.In summer, small perches prefer to stay in creeks and bays overgrown with aquatic vegetation. During this period, the perch forms smallflocks (about 10 fish), only in young individuals the school can reach the number of about 100 pieces... Perch loves to be near the piles of destroyed millsdams , near large stones and snags. Due to their greenish protective coloration, perches successfully hunt small fish, arrangingambushes among aquatic plants. Large perches live in deeper places:whirlpools , pits, often zakoryazyazhnyh, from where they come out in the morning and evening for hunting. School hunting is characteristic of young perches, only the largest individuals begin to hunt alone. River perch uses a very aggressive hunting model; it actively pursues its prey, sometimes jumping out after it even to the surface of the water. Sometimes the perch is so carried away by the pursuit that in pursuit it can jump out onstranded and even ashore ... During the attack, the perch puffs up the dorsalfin ... Larger perches can wait for their prey inambush, like a pike or a pike perch.River perch is a crepuscular-daytime predator that hunts during daylight hours with a peak of activity at the border of day and night. At night, the activity of the perch decreases sharply.

Common pike perch - species of fish from the familyperch. Large fish. According to official data, there are individuals more than a meter long and weighing up to 10-15 kg, probably there are samples of larger sizes. A characteristic feature is the presence of large canine-like teeth on the jaws, which are usually larger in males than in females.By way of life, pike perch is a typical predator. It feeds on fish, and small individuals also eat aquatic invertebrates. It is very sensitive to the concentration of oxygen in water and the presence of suspended matter, therefore it does not occur in swampy water bodies. In the warm season it keeps at depths of 2-5 m. It is active both during the day and at night, and at night it goes into shallow water, and during the day it migrates to deeper places. Usually prefers a sandy or pebbly bottom, especially if there are large objects (driftwood, stones, etc.) that can be used as a shelter, since zander is mainly an ambush predator. The basis of food is usually fish with a narrow body. As a rule, it isgobies, minnows, bleak or sprat ... The same fish are used when fishing for zander with live bait.

Ordinary ruff - a species of fish from the perch family, a typical species of the genus ruff. The back of the ruff is gray-green with black spots and dots, the sides are yellowish, the belly is light gray or white. Dorsal and caudal fins with black dots. The general color of this fish depends on the environment: the ruff is lighter in rivers and lakes with a sandy bottom, and darker in water bodies where the bottom is muddy. The eyes are cloudy pink, sometimes with a blue iris. The usual length is from 8 to 12 centimeters, the weight is from 15 to 25 grams. Sometimes, however, there are specimens more than 20 centimeters long and weighing even more than one hundred grams. Ruff is a very unpretentious, usually gregarious species, and it thrives very well in a wide range of environmental conditions. It can be found both in fresh and brackish water bodies with a salinity index of up to 10-12 ‰; in lake and flow type systems; at depths from 0.25 to 85 meters; at sea level and in mountain water bodies and from oligotrophic to eutrophic waters; it tolerates temperatures from 0-2 ° C to 34.5 ° C. Despite such a wide range of acceptable conditions, three main features of the habitat of this species can be distinguished. For the ruff, quiet reservoirs with a soft bottom, not covered with aquatic vegetation, are ideal; usually its population density increases with the rate of eutrophication. Soft-bottomed areas are more attractive for the ruff, since the overwhelming majority of its food objects are found in such places, and also because such areas are usually located in relatively deep and shaded parts of the reservoir - since all species of the Ruff genus have physiological adaptations to life in small the amount of light.
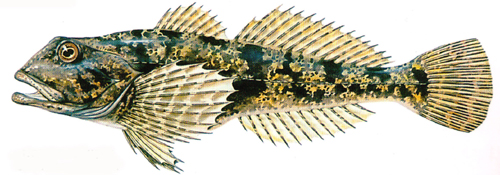 Common sculpin
- freshwater fish family of slingshot. ABOUTthe bullhead sculpin lives in flowing water bodies at an altitude of up to 2,000 m above sea level and in cool lakes. The species is demanding on the quality of water, it needs a high concentration of oxygen and, rather, low temperature water. Lives on a rocky bottom.The fish does not swim well and therefore moves in jerks with widely spaced pectoral fins above the bottom. This bottom fish is active at night. During the day, it is motionless and almost invisible on rocky ground, hiding between stones and plants.The sculpin feeds on small benthic animals such as insect larvae, less often caviar, larvae and juveniles of other fish, most oftenminnow, sticklebacks, trout , because these fish are its most frequent neighbors in the reservoir.
Spawning occurs between February and May. The male builds a hole under the stones, into which the female lays eggs. The male guards the nest until the fry appear in 4-5 weeks.
Common sculpin
- freshwater fish family of slingshot. ABOUTthe bullhead sculpin lives in flowing water bodies at an altitude of up to 2,000 m above sea level and in cool lakes. The species is demanding on the quality of water, it needs a high concentration of oxygen and, rather, low temperature water. Lives on a rocky bottom.The fish does not swim well and therefore moves in jerks with widely spaced pectoral fins above the bottom. This bottom fish is active at night. During the day, it is motionless and almost invisible on rocky ground, hiding between stones and plants.The sculpin feeds on small benthic animals such as insect larvae, less often caviar, larvae and juveniles of other fish, most oftenminnow, sticklebacks, trout , because these fish are its most frequent neighbors in the reservoir.
Spawning occurs between February and May. The male builds a hole under the stones, into which the female lays eggs. The male guards the nest until the fry appear in 4-5 weeks.

Pike obullish- fish of the pike family ... Distributed in fresh waters. It usually lives in the coastal zone, in water thickets, in stagnant or weakly flowing waters. May also occur in desalinated partsseas - for example, in Finsky, Riga and K urshsky bays Baltic Sea. The body of a pike is elongated, arrow-shaped, dline up to 1.5 m, weight up to 35 kg (usually up to 1 m and 8 kg). The body is torpedo-shaped, the head is large andhighly elongated, wide mouth , the lower jaw protrudes forward. The teeth on the lower jaw are of different sizes and serve to grip the victim. The teeth on the other bones of the oral cavity are smaller, directed with sharp ends into the pharynx and can sink into the mucous membrane. Thanks to this, the prey passes easily, and if it tries to escape, the pharyngeal teeth rise and hold the victim. The color is changeable, depending on the environment: depending on the nature and degree of development of vegetation, it can be gray-greenish, gray-yellowish, gray-brown, the back is darker, the sides with large brown or olive spots that form transverse stripes. Unpaired fins are yellowish-gray, brown with dark spots; paired - orange. It feeds mainly on fish. In some lakes, there are silver pikes.

River hill - a kind of predatory catadromous fish from the familyeels ... In 2008 he was included inRed Book IUCN as a “critically endangered” species.
It has a long, writhing body with a brownish-greenish back, with yellowness on the sides and abdomen. The skin is very slippery and the scales are small. It is capable of overcoming large areas of land on wet grass from rain or dew, moving from one reservoir to another and thus finding itself in closed, closed lakes. Prefers quiet water, however, it can also be found in a fast course. It keeps in the lower layers at different depths and in any bottom soil in shelters, which can be: a burrow, a boulder, a snag, dense thickets of grass. It hunts at night in shallow coastal waters, although the bait is enough during the day if it is in the immediate vicinity. It feeds on insect larvae, molluscs, frogs, and small fish. Reaches two meters in length and weighs 4 kg.

Burbot- the only exclusively freshwater riverthe squad is t resco-like.The body is elongated, low, rounded in the anterior part and strongly compressed laterally in the posterior part. The head is flattened, its length exceeds the maximum body height. The eye is small. The mouth is large, semi-lower, the lower jaw is shorter than the upper one. On the jaws and headcoulter there are small bristle teeth, but they are not on the palate. There is one unpaired antenna on the chin and a pair of antennae on the upper jaw. The color of the burbot's body depends on the nature of the soil, the transparency and illumination of the water, as well as on the age of the fish, therefore it is quite diverse: more often it is dark brown or blackish-gray, brightening with age. There are large light spots on the sides of the body and unpaired fins. The shape and size of the spots may vary. Belly and fins are light... Dorsal fins two: the first one is short, the second is long. The anal is also long. Together with the second dorsal, they come close totail but don't connect to it. The pectoral fins are rounded. The abdominal ones are located on the throat, in front of the pectorals. The caudal fin is rounded.Scales cycloid, very small, completely covers the whole body and part of the head from above to the nostrils andoperculum. Side line full to the beginning of the caudal peduncle, further to the tail may be interrupted. The body length can be up to 120 cm. Linear growth is not the same in different bodies of water.Burbot is more active in cold water.Spawning occurs in winter in December-February, the most successful fishing - during the first frost from dusk to dawn. It feeds on invertebrates and small fish. Can eat decaying animals... It is caught on gills, especially loves ruffs ... There are both sedentary (living in lakes and small rivers) and semi-anadromous forms (for example, river burbotObi). Sedentary forms, as a rule, are small and slow-growing.