Workers notebooks
Continued. Beginning see in № 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 26, 28, 29, 30, 31, 32/2004
Chemical properties. Consider the behavior of aldehydes regarding the standard set of reagents: air oxygen O 2, oxidizing agents [O], as well as H 2, H 2 O, alcohols, Na, NCl.
Aldehydes are slowly oxidized by air oxygen in carboxylic acids:
A high-quality reaction to aldehydes is the "silver mirror" reaction. The reaction consists in the interaction of aldehyde with an aqueous-ammonium solution of silver oxide (I), which represents a soluble comprehensive OH connection. The reaction is carried out at temperatures close to water boiling temperature (80-100 ° C). As a result on the walls of the glass vessel (test tubes, the flasks), the precipitate of metallic silver is formed - "SERVICE MIRROR":
Restoration of copper (II) hydroxide in copper oxide (I) is another characteristic reaction of aldehydes. The reaction occurs when the mixture is boiled and consists in the oxidation of aldehyde. More precisely, the introduction of an atom [O] of the Cu (OH) 2 oxidizing agent for the connection of the CU (OH) 2. In this case, the degrees of oxidation of carbonyl carbon (from +1 to +3) and the copper atom (from +2 to +1). When heating a blue sediment Cu (OH) 2 in a mixture with aldehyde, there is a disappearance of blue coloring and the formation of a red sediment Cu 2 O:
Aldehydes join hydrogen H 2 double bond C \u003d O when heated in the presence of a catalyst (Ni, Pt, Pd). The reaction is accompanied by a rupture
- Communications in the carbonyl group C \u003d O and connection at the place of its rupture of two atoms of hydrogen molecules nn. Thus, allegations are obtained from aldehydes:
Aldehydes with electronized substituents inPutting to the aldehyde group attach water With the formation of hydrates of aldehydes (diol-1,1):
In order to hold two electronegative hydroxyl groups, the carbon atom must carry a sufficient positive charge. The creation of an additional positive charge on carbonyl carbon is facilitated by three electro-coceptor chlorine atoms with a neighboring chlorine-carbon.
The reaction of aldehydes with alcohols. Synthesis of semi-acetals and acetals. In favorable conditions (for example: a) when heated with acid or in the presence of water-based drugs; b) with intramolecular condensation with the formation of five and six-membered cycles) aldehydes react with alcohols. At the same time, either one alcohol molecule (semi-acetal product) can be joined to one alpidage molecule (product - semi-acetal), or two alcohol molecules (product - acetal):
Aldehydes do not join Nsl double bond C \u003d O. Alporee also do not reactwith Na, i.e. The aldehyde hydrogen group does not have noticeable acid properties.
Application Aldehydes Based on their high reactivity. Aldehydes are used as source and intermediate compounds in the synthesis of substances with the useful properties of other classes.
Formaldehyde NNO - a colorless gas with a sharp smell - used for production polymeric materials. Substances with movable H atoms in the molecule (usually with C-H or N-H connections, but not O-H) are connected to formaldehyde CH 2 O by type:
If two or more movable protons (at phenol with 6 H 5, it is three such protons), then a polymer is obtained in the reaction with formaldehyde. For example, with phenol - phenol formaldehyde resin:
Similarly, urea with formaldehyde gives urea formaldehyde resins:
Formaldehyde serves as an initial substance for production dyes, pharmaceutical preparations, synthetic rubber, explosives and many other organic compounds.
Formalin (40% aqueous solution of formaldehyde) is used as antiseptic (disinfectant). The property of formalin rolling protein is used in leather manufacturing and to preserve biological products.
Acetaldehyde CH 3 SNO - colorless liquid ( t. Kip \u003d 21 ° C) with a sharp smell, well soluble in water. The main use of acetaldehyde - getting acetic acid. From it also get synthetic resins, medicines etc.
EXERCISES
1.
Describe, with what chemical reactions can be distinguished by the following pairs of substances:
a) benzaldehyde and benzyl alcohol; b) Propionic aldehyde and propyl alcohol. Specify what will be observed during each reaction.
2.
Bring the equations of reactions confirming the presence in the molecule
P-hydroxybenzaldehyde of the corresponding functional groups.
3.
Write the equations of boutanal reactions with the following reagents:
and) H 2, t., cat. Pt; b) KMNO 4, H 3 O +, t.; in) Oh. at NH 3 / H 2 O; d) NASN 2 CH 2 t, Cat. Nsl.
4. Make the equations of reactions for the chain of chemical transformations:
5. As a result of acetal hydrolysis aldehyde is formed Rcho and alcohol R'on. in a molar ratio 1:2. Make the equation of reactions of hydrolysis of the following acets:
6. In the oxidation of the maximum monohydric alcohol with oxide of copper (II), 11.6 g of organic compound with a 50% yield was formed. With the interaction of the resulting substance with an excess of ammonia solution of silver oxide, 43.2 g of sediment was separated. What alcohol was taken and what is his mass?
7. The 5-hydroxygexanal in the acidified aqueous solution is mainly in the form of a six-membered cyclic semi-aotic. Make the equation of the appropriate reaction:
1. Two substances can be distinguished by reactions characteristic only for one of these substances. For example, aldehydes are oxidized into acids under the action of weak oxidizers. Heating the mixture of benzaldehyde and ammonia solution of silver oxide proceeds with the formation of a silver mirror flasks on the walls:
Benzaldehyde is restored during catalytic hydrogenation into benzyl alcohol:
Benzyl alcohol reacts with sodium, hydrogen is highlighted in the reaction:
2C 6 H 5 CH 2 H + 2NA 2C 6 H 5 CN 2 ONA + H 2.
When heated in the presence of copper catalyst, the benzyl alcohol is oxidized by air oxygen into benzaldehyde, which is detected by the characteristic smell of Gorky Almond:
Similarly, the propionic aldehyde and propyl alcohol can be distinguished.
2. IN p- Hydroxibenzaldehyde Three functional groups: 1) aromatic ring; 2) phenolic hydroxyl; 3) Aldehyde group. In special conditions - when protecting the aldehyde group from oxidation (designation - [-sno]) - can be chlorinated p- Hydroxibenzaldehyde in the benzene ring:
The reaction with the alkali of phenolic hydroxyle:
The oxidation of the aldehyde group of SNO to carboxyl coxy, for example, when heated with a suspension of freshly prepared Cu (OH) 2:
b) oxidation scheme n.-Butanal potassium permanganate in a neutral environment:
C 3 H 7 SNO + kmNo 4 s 3 H 7 COI + MNO 2 + H 2 O.
Electron Ion Balance:
4. The equations of reactions for the chain of chemical transformations:
Alcohol Mass: m. = M. \u003d 0.4 60 \u003d 24 g
Answer. The alcohol of Propanol-1 weighing 24 g.
To determine the chemical formula of the organic matter, it is slightly burned, and then explore the combustion products. So, for example, when burning 3.75 g Formaldehyde received 2.25 g water vapor I. 5.5 g Carbon oxide (IV). Found that the density of vapor formaldehyde for hydrogen 15 . Using these data, find how many grams of carbon and hydrogen are contained in 3.75 g Formaldehyde:
M (CO 2) \u003d 12 + 32 \u003d 44; M \u003d 44 g / mol
44 g CO 2 contains 12 g
5.5 g CO 2 "X 1
44 ÷ 5.5 \u003d 12 ÷ x 1; x 1 \u003d (5,5 · 12) / 44 \u003d 1.5; M (C) \u003d 1.5 g
M (H 2 O) \u003d 2 + 16 \u003d 18; M \u003d 18 g / mol
18 g H 2 O contains 2 g
2.25 g H 2 O "X 2
18 ÷ 2.25 \u003d 2 ÷ x 2; x 2 \u003d (2.25 · 2) / 18 \u003d 0.25; M (H) \u003d 0.25 g
Find a total mass of carbon and hydrogen:
X 1 + x 2 \u003d 1.5 + 0.25 \u003d 1.75
Since 3.75 g of formaldehyde was taken for burning, it is possible to calculate the mass of oxygen:
3.75 - 1.75 \u003d 2; M (O) \u003d 2 g
Determine the simplest formula:
C: H: O \u003d (1.5 ÷ 12): (0.25 ÷ 1): (2 ÷ 16) \u003d 0.125: 0, 25: 0,125 \u003d 1: 2: 1
Consequently, the simplest formula of the studied substance CH 2 O.
Knowing the density of vapor formaldehyde for hydrogen, calculate its molar mass:
M \u003d 2d (H 2) \u003d 2 · 15 \u003d 30; M \u003d 30 g / mol
Find a molar mass along the simplest formula:
M (CH 2 O) \u003d 12 + 2 + 16 \u003d 30; M (CH 2 O) \u003d 30 g / mol
Consequently, the molecular formula of formaldehyde CH 2 O.
In the formaldehyde molecule between atoms of carbon and hydrogen, there are σ-bonds, and between carbon and oxygen atoms - one σ- and one π-bond.
Isomeria and nomenclature
For aldehydes, the isomerism of the hydrocarbon radical is characteristic. It may have either unbranched or branched chain. The names of the aldehydes occur from the historical names of the corresponding organic acids in which they turn into oxidation (forming aldehyde, acetic aldehyde, propionic aldehyde, etc.). At the international nomenclature, the names of the aldehydes are produced from the names of the corresponding hydrocarbons with the adding suffix -al.
The most important representatives of the aldehydes.
Methanal, or formaldehyde *
Ethanal, or acetaldehyde *
Propanel
Butanal
2-methylpropanal
Pentanal
Hexanal

Obtaining
IN laboratories Aldehydes are obtained by oxidation of primary alcohols. As oxidizing agents copper Oxide (II), hydrogen peroxide and other substances capable of giving oxygen. In general, it can be represented like this: 
IN industry Aldehydes are obtained in various ways. It is economically most profitable to receive metanal Direct oxidation of methane air oxygen in a special reactor.
So that methanal does not have time to oxidize, a mixture of methane with air through the reaction zone is passed at high speed.
Methanal is also obtained by oxidation of methanol, passing its pairs along with air through a reactor with a red-hot or silver mesh. However, this method is economically less profitable.
Ethanal It is possible to obtain hydration of acetylene in the presence of mercury salts as a catalyst ( reaction M. G. Kucher). Since in this reaction, poisonous substances are used as a catalyst - a new method of obtaining acetaldehyde has been developed in recently: a mixture of ethylene with air is passed through an aqueous solution of copper salts, iron and palladium.
Physical properties
Metanal - Colorless gas with a sharp smell. The solution of methanal in water (35 - 40%) is called formalin. The remaining members of a number of aldehydes are liquid, and the highest - solid.
Chemical properties
For aldehydes most characteristic of the reaction oxidation and accession.
1. Oxidation reactions
and) A high-quality reaction to aldehydes is the reaction "Silver Mirror". For its implementation, it is poured into a clean test tube ammonia Silver Oxide Solution (I) (Ag 2 O in water is practically not dissolved, but with ammonia forms a soluble OH compound), a solution of aldehyde is added to it and heated.
Restored silver settles on the walls of the test tube in the form of a brilliant bell, and the aldehyde is oxidized into the appropriate organic acid.
b) Another characteristic reaction is the oxidation of aldehydes copper hydroxide (II). If the hydroxide (II) hydroxide (II) hydroxide is pouring the aldehyde solution and heat the mixture, then the yellow precipitate of copper hydroxide (I) appears, which, with further heating, turns into red copper oxide (I). In this reaction, the oxidizer is copper with a degree of oxidation +2
which is restored to the degree of oxidation +1
.
2. Reaction of joining
The reaction of the addition is due to the presence in the carbonyl group π-bondwhich is easily broken. At the place of its rupture, atoms and atomic groups are joined. For example, when a mixture of methanal with hydrogen over a heated catalyst occurs its restoration to methanol.
Similarly attach hydrogen and other aldehydes.
Definition
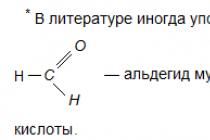
Aldehydes - Organic substances related to the class of carbonyl compounds containing in their composition a functional group -CH \u003d O, which is called carbonyl.
The general formula of limit aldehydes and ketones C n H 2 N O. The title of aldehydes is present suffix-and.
The simplest representatives of the aldehydes - formaldehyde (forming aldehyde) -CH 2 \u003d O, acetaldehyde (acetic aldehyde) - CH 3 -CH \u003d O. Cyclic aldehydes exist, for example, cyclohexane-carbaldehyde; Aromatic aldehydes have trivial names - Benzaldehyde, Vanillin.
The carbon atom in the carbonyl group is in a state of SP 2-hybridization and forms 3σ-bonds (two links of C --N and one connection C-O). π-bond is formed by P-electrons of carbon and oxygen atoms. Dual bond with \u003d o is a combination of σ- and π-links. Electronic density is shifted toward an oxygen atom.
For aldehydes, the carbon skeleton isomeria is characteristic, as well as an inter-odd isomeria with ketones:
CH 3 -CH 2 -CH 2 -CH \u003d O (Boutanal);
CH 3 -CH (CH 3) -CH \u003d O (2-methylpenanal);
CH 3 -C (CH 2 -CH 3) \u003d O (methyl ethyl ketone).
Chemical properties of aldehydes
There are several reactionary centers in the aldehyd molecules: an electrophilic center (carbonyl carbon carbonyl), participating in nucleophilic access reactions; The main center is an oxygen atom with watered electronic pairs; α-cn acid center responsible for condensation reactions; Communication C-H, bursting in oxidation reactions.
1. Reaction of attachment:
- Water with the formation of gem diols
R-CH \u003d O + H 2 O ↔ R-CH (OH) -OH;
- Alcohols with the formation of semi-acetals
CH 3 -CH \u003d O + C 2 H 5 OH ↔CH 3 -CH (OH) -O-C 2 H 5;
- Tiol with the formation of dithioacetals (in an acidic environment)
CH 3 -CH \u003d O + C 2 H 5 SH ↔ CH 3 -CH (SC 2 H 5) -SC 2 H 5 + H 2 O;
- sodium hydrosulfite with the formation of sodium α-hydroxisulfonates
C 2 H 5 -CH \u003d O + NaHSO 3 ↔ C 2 H 5 -CH (OH) -SO 3 Na;
- Amonov with the formation of N-substituted imine (Schiff base)
C 6 H 5 CH \u003d O + H 2 NC 6 H 5 ↔ C 6 H 5 CH \u003d NC 6 H 5 + H 2 O;
- hydrazines with the formation of hydrazones
CH 3 -CH \u003d O + 2 HN-NH 2 ↔ CH 3 -CH \u003d NH 2 + H 2 O;
- cyanogenic acid with nitrile formation
CH 3 -CH \u003d O + HCN ↔ CH 3 -CH (N) -OH;
- Restoration. In the interaction of aldehydes with hydrogen, primary alcohols are obtained:
R-CH \u003d O + H 2 → R-CH 2 -OH;
2. Oxidation
- the reaction of the "silver mirror" - the oxidation of the aldehydes ammonia solution of silver oxide
R-CH \u003d O + AG 2 O → R-CO-OH + 2AG ↓;
- oxidation of the aldehydes of copper hydroxide (II), as a result of which the precipitate of copper (I) oxide drops
CH 3 -CH \u003d O + 2CU (OH) 2 → CH 3 -COOH + Cu 2 O ↓ + 2H 2 O;
These reactions are high-quality reactions to aldehydes.
Physical properties of aldehydes
The first representative of the homologous series of aldehydes - formaldehyde (forming aldehyde) is a gaseous substance (N.U.), aldehydes of an unbranched structure and composition C 2 -C 12 - liquids, with 13 and longer - solids. The more carbon atoms are part of the unbranched aldehyde, the higher its boiling point. With an increase in the molecular weight of aldehydes, the values \u200b\u200bof their viscosity, density and refractive index increase. Formaldehyde and acetaldehyde can be mixed with water in unlimited quantities, however, with increasing hydrocarbon chain, this ability of aldehydes is reduced. Lower aldehydes have a sharp smell.
Getting aldehydes
Main ways to obtain aldehydes:
- hydraulication of alkenes. This reaction consists in connecting CO and hydrogen to alkene in the presence of carbonyls of some metals of the VIII group, for example, octarbonyldicobalt (CO 2 (CO) 8) reaction is carried out when heated to 130c and 300 atm pressure
CH 3 -CH \u003d CH 2 + CO + H 2 → CH 3 -CH 2 -CH 2 -CH \u003d O + (CH 3) 2 SNS \u003d O;
- hydration of alkins. The interaction of alkins with water occurs in the presence of mercury salts (II) and in an acidic environment:
NS≡Sn + H 2 O → CH 3 -CH \u003d O;
- oxidation of primary alcohols (the reaction proceeds when heated)
CH 3 -CH 2 -One + Cuo → CH 3 -ch \u003d O + Cu + H 2 O.
Application Aldehydes
Aldehydes were widely used as raw materials for the synthesis of various products. So, from formaldehyde (large-capacity production) various resins (phenol-formaldehyde, etc.), drugs (urotropin) are obtained. Acetaldehyde - raw materials for the synthesis of acetic acid, ethanol, various derivatives of pyridine, etc. Many aldehydes (oil, cinnamon, etc.) are used as ingredients in perfumery.
Examples of solving problems
Example 1.
| The task | 9.5 g of a monobromide was obtained by bromination with N H 2 n +2, which, during the treatment with a diluted NaOH solution, turned into an oxygen-containing compound. A pair of it with air is missed over the hot copper grid. When processing the new gaseous substance formed in this case, an excess of ammonia solution Ag 2 O was released 43.2 g of sediment. What hydrocarbon was taken in what quantity, if the output at the bromination stage of 50%, the remaining reactions proceed quantitatively. |
| Decision | We write the equations of all occurring reactions: C n H 2N + 2 + BR 2 \u003d C n h 2n + 1 br + HBr; C n h 2n + 1 br + naoh \u003d c n h 2n + 1 oh + nabr; C n H 2N + 1 OH → R-CH \u003d O; R-CH \u003d O + AG 2 O → R-CO-OH + 2AG ↓. The precipitate allocated in the last reaction is silver, therefore, you can find the amount of substance of silver distinguished: M (Ag) \u003d 108 g / mol; v (Ag) \u003d m / m \u003d 43.2 / 108 \u003d 0.4 mol. Under the condition of the problem, after passing the substance obtained in the reaction 2 above the hot metal mesh, gas was formed, and the only gas -aldehyde gas is methanal, therefore, the starting material is methane. CH 4 + BR 2 \u003d CH 3 BR + HBr. Number of bromomethane substance: v (CH 3 BR) \u003d M / M \u003d 9.5 / 95 \u003d 0.1 mol. Then, the amount of methane substance necessary for 50% of the yield of bromomethane is 0.2 mol. M (CH 4) \u003d 16 g / mol. Consequently, the mass and volume of methane: m (CH 4) \u003d 0.2 × 16 \u003d 3.2 g; V (CH 4) \u003d 0.2 × 22,4 \u003d 4.48 liters. |
| Answer | Massa mass - weight 3.2 g, methane-4.48 l |
Example 2.
| The task | Write the reaction equations with which the following transformations can be carried out: butene-1 → 1-brombutane + NaOH → A - H 2 → B + OH → C + HCl → D. |
| Decision | To obtain 1-bromobutan from Bootena-1, it is necessary to carry out a hydrobromation reaction in the presence of peroxide compounds R 2 O 2 (the reaction proceeds against the Markovnikov rule): CH 3 -CH 2 -CH \u003d CH 2 + HBR → CH 3 -CH 2 -CH 2 -CH 2 BR. When interacting with an aqueous alkali solution, 1-Brombutan is subjected to hydrolysis with the formation of butanol-1 (a): CH 3 -CH 2 -CH 2 -CH 2 BR + NaOH → CH 3 -CH 2 -CH 2 -CH 2 OH + NABR. Butanol-1 with dehydrogenation forms Aldehyde - Butanal (B): CH 3 -CH 2 -CH 2 -CH 2 Oh → CH 3 -CH 2 -CH 2 -CH \u003d O. The ammonium solution of silver oxide oxidizes boutanal to ammonium salt - ammonium butyrate (C): CH 3 -CH 2 -CH 2 -CH \u003d O + Oh → CH 3 -CH 2 -CH 2 -Coonh 4 + 3NH 3 + 2AG ↓ + H 2 O. Ammonium butyrate when interacting with hydrochloric acid forms oil (butane) acid (D): CH 3 -CH 2 -CH 2 -COONH 4 + HCl → CH 3 -CH 2 -CH 2 -COOH + NH 4 Cl. |