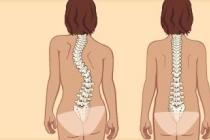
Posture, which develops in children practically from birth to 17-21 years old, should cause appropriate attention from parents. After all, the back for any person is not only support and the ability to move beautifully and easily, but also the aesthetic component of the image. An adult with back problems makes a titanic effort to look natural and healthy, poor posture is a whole problem. Meanwhile, it can be avoided by monitoring the condition of the child's back from an early age.
Back - support and functionality of internal organs
Babies, at birth, have a flexible spine, physiologically curved outward. Their back with a fragile muscle frame needs special attention until the baby learns to sit on his own without support. Sometimes, in an attempt to teach the child to sit faster, the elders put the newborn in pillows, swings, hold it vertically in their arms for a long time or carry it in a sitting or upright position in my-sling (kangaroo). This is absolutely impossible to do.
Holding the back of the baby with the palm of your hand is not enough, because the load on the spinal column of a child who still has a cartilaginous structure is too great, and this position is unnatural and will cause many problems in the functioning of a growing organism and the correct development of internal organs - in particular, the gastrointestinal tract. In addition, a large load on the lower back and pelvic bones can cause an abnormal formation of the musculoskeletal system, the occurrence of hip dysplasia, as the most harmless diagnosis. And this will entail a lot of problems with the formation of walking. In addition, numerous nerve endings, pinched by the vertebrae due to constant improper load on the spine, can provoke problems even in the formation of speech, various reflexes.
How the spine is formed
Gradually learning how to stay in a sitting position, the baby strengthens his back with movements, develops the musculoskeletal system by active crawling, and at the same time strengthens his muscular frame and back ligaments.
By the age of five months, on average, babies are able to sit, and posture begins to form due to constant muscle activity. The first natural bends appear in the spine, the abdominal muscles gradually develop, but only by the age of one year (on average) the load on the spine is balanced with the total load on the body, legs, arms and back. Natural curves in the spine appear in the cervical, thoracic and lumbar spine, but from behind it should appear straight and without bends, bulges or curvatures to the left or right.
Correct posture in young children
Under the influence of the forces of gravity, the forming muscle corset of the child is still very weak, therefore, the bends in the cervical and lumbar spine are quite physiological. Babies, having taken an upright position, have lumbar lordosis, visually it looks like a bulging tummy. Over time, the more the child will walk, run, the higher his physical activity, the more correct and faster the physical health of the spine will develop. By school age, having stretched out in height, having lost the childish plumpness in the shoulder and hip girdle, the child looks already fully formed. However, it is not. If children in preschool-school age have poor posture, scoliosis in adolescents has a great chance of developing.

This disease develops for several reasons. We have already touched on the wrong child care up to a year. I would like to once again draw attention to this: it is categorically impossible to force the child to sit down or constantly carry him in an upright state until the baby starts to sit down on his own. Many problems of the musculoskeletal system begin precisely from early childhood. Today, the correction of scoliosis in babies is possible with the help of regular gymnastics, massages and water procedures, more serious cases require the attention of orthopedists and the use of auxiliary simulators, complexes of physiotherapeutic procedures.
Dangerous age
Most people know what the development of scoliosis is connected with. This, of course, is the active growth of the body and irrational stress during this period on the spine. After the child has begun to walk, of course, protecting from falls, bruises and injuries is the sacred duty of any parent. But there comes a time when the little man is already completely independent, and the parent's vigilance begins to slowly decrease, but in vain.
Between the ages of five and eight, children again require attention to their physiological development. This period is marked by rapid growth, from a young age, the child quickly and abruptly moves to preschool or school. But the body needs time to adapt to the sharply stretched limbs. At this time, scoliosis occurs in children, which often goes unnoticed. The school program provides for daily physical activity with textbooks, notebooks, but young schoolchildren often take additional weights to school - books, games, things.
The curvature of the spine depends not only on irregular loads, but also on the quality of nutrition, on how often the child is sick, that is, on lowered immunity, on regular irregular positions of the trunk during exercise.

The next stage of age-related influence on the spine refers to the period of 11-12 years, when, in addition to all of the above factors, scoliosis in children occurs due to a lifestyle in a hypodynamic rhythm. This is caused by the influence of the abundance of computer games, gadgets, which deprives adolescents of elementary walks in the fresh air and the movement necessary for the body to function correctly, the loads exerted on the body when walking.
The next and last stage of the increased risk of developing scoliosis occurs at the age of 15-18. During this period, scoliosis in adolescents often occurs against the background of growth complexes or generally physique, shyness, and the development of body features. Therefore, it is important to pay attention to the child not only as an elder, but also as a psychologist.
All of these causes of scoliosis should be controlled and addressed to avoid postural problems.
Forms of scoliosis
There are several forms of scoliosis, when the bends of the spine take the form of the Latin letters C, S or Z. S-shaped scoliosis is characteristic of childhood, when the spine is curved in one direction, forming two lines of direction of the spine. Z-shaped scoliosis is characterized by bends of the spine in two directions, forming three lines of direction of the spinal column.
It is dangerous to ignore these types of scoliosis. For example, curvatures in the lumbar spine for girls in the future are fraught with pathologies of pregnancies, miscarriage. The middle part of the spine, which has displaced vertebrae, will cause problems in the work of internal organs, and scoliosis of the thoracic region can cause the formation of both costal and cervical humps. Fortunately, according to traditional medicine, the progression of the disease stops at the end of development, that is, around the age of twenty, but unresolved problems with curvature of the spinal column will definitely become a disaster after forty.

Scoliosis grade
Determination of the severity of the curvature for the appointment of appropriate treatment is necessary; for this, patients are given an x-ray. According to the system of the American orthopedist J. Cobb, four degrees of scoliosis are distinguished on x-rays.
The first degree is not always determined visually, because the curvatures are very slight. The second degree of scoliosis is visually already noticeable in the form of an asymmetric posture, different muscle sizes and an obvious hump in the costal part when bending forward. The degree of scoliosis on X-ray is already about 20, such a deformation can begin to change in the chest. The third degree is already strongly noticeable, and even in a standing position, the curvature causes great discomfort for both the respiratory tract and the child's activity in general. Fading behavior, low immunity, frequent illnesses and inactivity are characteristic signs for this degree, scoliosis in adolescents here sometimes has an idiopathic (that is, of unclear genesis) origin, and it is worth again taking more care of your child during puberty in order to avoid problems with the spine in future. After all, the development of the disease is dangerous: the greater the angle of deformity of the spine, the more destructive it has on the body.
Prevention of scoliosis
The manifestations of scoliosis are caused by the fact that adverse factors affect the spine of a growing child. Orthopedic problems missed in early childhood can affect just in adolescence in the form of weakened muscle areas, provoking abnormal growth and development of muscle tissue, bone and cartilage. And this is of great importance for the formation of posture.
In order for scoliosis in children to not have disastrous consequences, you need to monitor the child's activity and the postures in which he stays during monotonous activities.
For example, in a sitting position, the child should sit at a table, the height of which should correspond to his height and not provoke bending or leaning back in the chair. The optimal position is when the angles under the knees and between the body and the hips of the sitting child are 90 degrees, that is, a right angle. Make sure that he does not cross his legs, does not put one leg under the buttocks, bending in the lumbar, thoracic, and cervical spine, does not slouch, leaning on the elbow.

In a standing position, the habit of standing in an asymmetrical position can affect the already acquired curvature of the spine, exacerbating the course of the disease.
The great influence of the information volume, which is given today in developmental classes, from a very early age determines a hypodynamic lifestyle, so it is worth taking care that the child's development is still harmonious, and pay attention to his physical development.
Not all types of scoliosis are acquired as a result of improper posture or increased stress on the spine. A huge part of the practice of orthopedists is the work of correcting the curvature of the spine and treating curvatures using various methods. The causes of scoliosis are diseases such as pleurisy, tuberculosis, rickets, so it is especially important that babies are more often in the fresh air and walk under the sun's rays, which provide the body with vitamin D.
But scoliosis in children is also congenital, this is due to a violation in the processes of intrauterine development and fetal formation. Such cases are very severe and are diagnosed with varying degrees of damage to the spinal column. In some cases, it is possible to help the child, but in some - all measures are powerless, and the person remains confined to a wheelchair for life. Preventive measures in the form of exercises and gymnastics are very useful, but in serious cases they have no effect, therefore, they resort to surgical intervention.
Spinal scoliosis, treatment
The immutable truth is that curing a disease is much more difficult than preventing it. Preventive measures will make fears about the occurrence of scoliosis in vain, the disease, if any, will be turned into a regressive stage, and all this at a minimum cost with a maximum benefit. If your child is diagnosed with scoliosis, how to treat the spine, first of all, gives recommendations from an orthopedist and, possibly, a surgeon. If the disease has a first or second degree, the main thing is not to be lazy, not to start the disease, but to urgently take simple but effective measures.

Signs of scoliosis
How to determine on your own whether there is a suspicion of scoliosis, how to treat it at the initial stages and is it difficult? The most important thing is to recognize the disease on time. If your observations of the child suggest that it is worth contacting an orthopedist, you can independently conduct a test to determine deviations in the position of the shoulders and shoulder blades relative to each other.
The first thing to do is to inspect. A slouch can be seen on the side. The curvature can be determined by a suspended pendulum. A weight suspended on a thread from the seventh cervical vertebra (the most protruding one) in free fall will show a strict vertical. The weight should be at the level of the tailbone, if it is displaced - there is a displacement of the spine.
You can also conduct a horizontal test. In the supine position, face down, keeping the child's pelvis on the bed, and the upper body outside it, it is necessary for the child to maintain this horizontal and without support under the breast for at least 30 seconds. (preschoolers) up to 2.5 min. (teenagers).
How to help a child correct scoliosis
On the part of the parents, it is important to create favorable conditions for the full development and growth of the body. These are sleep patterns, regular and full meals, hygiene, walks, sports and recreation, hardening.
From a very early age, gymnastics is shown, for very young children it should be in a playful way: raise the arms up, lower them down, spread them to the sides, describe the circle with a straightened arm and bent at the elbow, to the shoulder. For older children, excellent exercises with a stick are suitable, for which the child takes up with both hands and performs bends, swings, shakes the press without letting go of the ends of the stick.

In case of insufficient prevention, treatment is prescribed in the form of a course of manual or therapeutic massage, acupuncture, electrophoresis of the back muscles, and wearing special corsets. Do not forget about activity and sports, swimming and walking. It is worth teaching a child to follow his posture from early childhood, and then his life at a respectable age will not bring many problems associated with the spine.
Take care of your children!
If you ask at what age the prevention of scoliosis should begin, then the correct answer would be: from the moment of birth. The fact is that this condition develops from childhood to adolescence, and the earlier measures to prevent the disease are started, the less chance that in the future a person will face problems with posture curvature and associated ailments.
Prevention of scoliosis in children is the task of parents in taking care of the child's health.
What are the types of scoliosis
Scoliosis is a curvature of the spine caused by deformation of the discs. Normally, the ridge should be at a slight angle - if you look at anatomical reference books depicting human bones, you can see with your own eyes. However, if the curvature exceeds 5-10 degrees or there is a change to the right or to the left, then they speak of a disease.
There are two types of posture changes, scoliosis prevention refers to both of them: lordosis and kyphosis... Both are present in the norm, only an increase in the degree of inclination in one direction or another will be considered an anomaly.
The first implies a curvature forward, the second, respectively, backward. Both conditions, and this will be indicated in any abstract on the prevention of scoliosis, require correction.
By their origin, posture disorders are divided into the following subtypes:
- Myopathic - the cause of the disease should be sought in the muscles;
- Neurogenic - the prevention of childhood scoliosis of this form implies regular visits not only to the osteopath, but also to the neuropathologist;
- Dysplastic - are associated with endocrine diseases and bone development disorders;
- Traumatic - the presentation on the prevention of scoliosis will indicate that they appear due to back injuries;
- Idiopathic - arise "by themselves."
Based on these data, the prevention of scoliosis in preschool children and the prevention of scoliosis in schoolchildren should be carried out continuously along with routine examinations by an osteopathic doctor.
Parents should carefully observe the posture of their children.
When preventing postural disorders and scoliosis, it is necessary to take into account the provoking factors and risk factors. These include:
- underdevelopment of muscles - from a banal lack of movement in a child to muscular dystrophy;
- belonging to the female sex, it is believed that girls develop the disease more often;
- birth injuries to the bones;
- lack of calcium and other vitamins;
When several factors are summed up, an ailment arises, and in some cases, a so-called progressive form of the disease appears. It requires particularly careful observation and immediate treatment.
Exercise is extremely important to prevent and correct untreated forms of the disease.
Exercises for the prevention of scoliosis include complexes for correcting posture, improving muscle tone and strengthening the muscles.
A set of exercises for the prevention of scoliosis may include the following methods of dealing with the disease:
- The patient lies down on the floor or on a hard surface with his stomach down. It is required to part and again close the hands on the back of the head - while the back should remain straight. This exercise for the prevention of scoliosis in children is effective in the early stages of the development of the disease, or simply to improve posture.
- The legs are spread apart and rise up in the supine position. As in the first case, the spine remains straight, the back touches the floor. Compulsory execution on a solid.
- Lying on your back, the pelvis is raised to the maximum possible height. This exercise is recommended by Krasikova for the prevention and treatment of scoliosis. For one to two minutes, you must hold the position with support on the shoulder girdle. As in the previous cases, the level of the back is strictly maintained. Repeat up to six to seven times.
- The patient lies on his chest, holding his hands at the back of his head in a knot. Raises only the chest to the waist, trying to keep the legs and posture straight. Repeat up to seven to ten times, depending on physical fitness.
- In the prone position, raise the extended and strictly straight legs in turn. The arms are extended at the seams, the back is kept straight.
In addition to sports activities for the prevention of scoliosis and flat feet, it is necessary to monitor the load regimen. This is especially important in relation to young children and younger students.
It is impossible for them to constantly sit at the desk, be sure to let them warm up after every twenty minutes or half an hour of lessons.
The diet for children with postural disorders should include calcium-rich foods - dairy and lactic acid, eggs, meat, sea fish. Vegetables and fruits are useful because they contain vitamins.
In the early stages, prevention of childhood scoliosis is not a serious problem. Parents need to notice changes in time and take action.
- persistent deformation of the spinal column, characterized by its lateral deviation and torsion. Scoliosis in children is accompanied by an asymmetric position of the shoulder girdle, shoulder blades and other bony landmarks, a skewed pelvis, chest deformity, and abnormalities in the internal organs. To diagnose scoliosis in children, polypositional radiographs of the spine are performed with the calculation of the amount of curvature. Conservative treatment of scoliosis in children includes an orthopedic regimen, massage, corrective gymnastics, physiotherapy, wearing an orthopedic corset; surgical correction of scoliosis is performed according to indications.

General information
Scoliosis in children is pathological changes in the spine and paravertebral tissues, leading to curvature of the spinal column, its rotation around the longitudinal axis, static-dynamic disorders and functional changes in the internal organs. Scoliosis is one of the most common diseases of the musculoskeletal system in pediatric orthopedics, which affects 5-10% of children and adolescents. Scoliosis is much more common in girls than in boys; the approximate sex ratio is 9: 1. The danger of developing scoliosis in a child consists not only in a cosmetic defect, but also in compression, displacement and dysfunction of blood vessels and internal organs.

Classification of scoliosis in children
Depending on the time of manifestation, infantile (infant) scoliosis in children under 3 years of age is distinguished; children's (juvenile) scoliosis in pre-pubertal children (from 3 to 10 years old); juvenile scoliosis in children and adolescents from 10 to 18-20 years old, i.e. before the cessation of bone growth.
The cases of acquired scoliosis in children are usually associated with neuromuscular, metabolic, neoplastic diseases and injuries. Static scoliosis in children is most often the result of birth trauma, congenital dislocation of the hip, shortening of the lower limb, contractures of the knee and hip joints. Neurogenic scoliosis in children can occur due to infantile cerebral palsy, poliomyelitis, syringomyelia, Friedreich's ataxia, spinal cord injuries and other pathological conditions. The genesis of myopathic scoliosis in children may be due to congenital muscular hypotension, muscular dystrophy, and congenital torticollis.
Scoliosis in children may be based on traumatic deformities of vertebral localization (after a spinal fracture, thoracoplasty, laminectomy, etc.) or extravertebral localization (after extensive burns of the trunk, pleural empyema, etc.). Often, metabolic disorders (rickets, cystinosis, osteogenesis imperfecta, Hunter syndrome), hereditary connective tissue diseases (Marfan syndrome, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome), rheumatic pathology (juvenile rheumatoid arthritis), tumors of the spinal column and spinal cord, juvenile osteochondrosis, neurofibromatosis.
However, despite the variety of identified factors that contribute to the development of scoliosis in children, most cases are idiopathic, that is, arising for unknown reasons.
General asthenia, physical inactivity, posture disorders, inadequate loads on the spine, etc., predispose to the development of scoliosis in children.
Scoliosis symptoms in children
Idiopathic scoliosis in children is usually detected at 6-7 years of age, that is, during the period of the first growth spurt, when a child is examined by a pediatrician or pediatric orthopedist. The clinical manifestations of scoliosis in children differ depending on the degree of spinal deformity.
Scoliosis of the I degree in children can be suspected by the following characteristic features: lowered position of the head, flattened shoulders, sloping pelvis, stoop, asymmetry of the shoulder girdle and waist, the outlined rotation of the vertebrae around the longitudinal axis. The arc of curvature is visible when leaning forward and disappears when the child's torso is straightened.
With scoliosis of the II degree, in addition to the above listed signs, children develop pathological rotation of the vertebrae, a muscle roller in the lumbar spine and a bulge in the thoracic spine on the side of the curvature. The curvature of the spine does not disappear in any position of the body.
Clinical signs of grade III scoliosis in children are characterized by a pronounced rotation of the vertebrae, a well-defined rib hump, muscle contractures, weakening of the abdominal muscles, bulging of the costal arches, etc.
In grade IV scoliosis, the child's spine is significantly deformed, the paravertebral muscles are stretched, the rib hump is pronounced, the ribs and muscles in the concavity zone sink.
The progression of pathological changes in scoliosis in children leads to the development of a functionally significant deformity of the chest, accompanied by compression and displacement of the heart, lungs and vascular bundle. This condition is regarded as a scoliotic disease in children.
Scoliosis of I and II degrees in children usually proceeds without subjective complaints; with scoliosis of III and IV degrees, back pain, increased fatigue, shortness of breath, pain in the heart, tachycardia, and stiffness of movements may disturb. Complications and consequences of scoliosis in children and adolescents can be vegetative-vascular dystonia, neurocirculatory dystonia, biliary dyskinesia, cholecystitis, etc. Girls suffering from scoliosis have an increased risk of developing menstrual irregularities, and in the future - spontaneous abortion, labor disorders (weakness, discoordination, etc.).
Scoliosis in children is often combined with another pathology of the musculoskeletal system: dysplasia of the hip joints, flat feet, curvature of the spine in the sagittal plane (kyphosis).
Diagnosis of scoliosis in children
Early detection of scoliosis is the most important task of dispensary examinations of preschool and school children by a pediatrician, pediatric surgeon, neurologist, and pediatric orthopedist. For a correct assessment of posture, a consistent examination of the child in a standing position (front, side, back), sitting and lying is necessary. At the same time, attention is paid to the height of the shoulder girdle, the asymmetry of the skin folds, shoulder blades, pelvis, the presence of a rib hump and other signs of scoliosis in children. The degree of curvature of the spine in degrees is determined using a scoliosometer. Revealing a deviation of the spine by more than 5-7 ° is the basis for radiography of the child.
Scoliosis treatment in children
The generally accepted tactics involves differentiated approaches to the conduct of therapeutic measures for children with varying degrees of severity of scoliosis. Conservative treatment is carried out with the participation of physiotherapists, massage therapists, exercise therapy instructors, vertebrologists, manual therapists.
Children with grade I-II non-progressive scoliosis need to eliminate the causes that contribute to the curvature of the spine, reduce the static load on the spinal column, and organize optimal motor activity. In order to prevent the progression of scoliosis, children are recommended therapeutic exercises, back massage, swimming. An important component of the treatment of scoliosis in children is adherence to the orthopedic regime - sleeping on a shield, monitoring correct posture, and periodically unloading the spine in a horizontal position.
spinal traction.
According to indications, corrective osteoplastic operations (wedge-shaped resection of the vertebrae), mobilizing operations (tenoligamentocapsulotomy according to Shulutko, discectomy), cosmetic interventions (resection of the rib hump, extrapleural thoracoplasty, resection of the scapula angle), etc. can be performed. After operations, long-term rehabilitation therapy is performed.
Prediction and prevention of scoliosis in children
Early-onset spinal deformities (up to 6 years of age) have an unfavorable progressive course; scoliosis is more favorable in children over 10-12 years old. All children with scoliosis should regularly, at least 2 times a year, undergo specialized treatment prescribed by an orthopedist. With severe scoliosis in children, surgery can only reduce the degree of curvature of the spine and stop its progression. Therefore, the main efforts of adults should be aimed at preventing scoliosis in children.
A rational organization of the motor regime of children at home and in child care facilities, control over maintaining the correct posture, exclusion of heavy loads on the spine and asymmetric muscle loading, health-improving gymnastics and sports, and injury prevention are required. In case of violations of posture, children are shown courses of exercise therapy, general strengthening massage, swimming.
A healthy spine has four curves, two each with a bulge forward and backward. Thanks to these physiological curves, the spine can withstand dynamic and static loads, they protect the intervertebral discs and ligaments from injury, performing a shock-absorbing function. The deviation of the spine from the normal axis causes various disorders. If the deviation occurs in the horizontal plane, then there is a stoop, kyphosis, hyperlordosis, and if in the vertical - scoliosis.
Scoliosis is a curvature of the spinal column in a certain area to the right, left, or simultaneously in two directions. This is a fairly common disease. It is detected in 10% of five-year-olds, and by the end of school, it is found in 50% of children. This is due to the fact that scoliosis can develop at any stage of the body's growth. Posture formation lasts up to 18-20 years. The presence of scoliosis cannot be considered only an aesthetic problem, because it can provoke the onset of pain, and in especially severe cases even lead to disruption of the normal functioning of internal organs.
Scoliosis causes
Scoliosis can be congenital or acquired. The causes of the congenital type can be:
- improper intrauterine development of the spine (deformation, underdevelopment or the presence of extra vertebrae);
- additional ribs, as well as the absence of one or more of them;
- connective tissue pathology of a hereditary nature;
- joint hypermobility;
- congenital torticollis;
- different leg lengths (even a visually imperceptible difference of half a centimeter is tangible);
- calcium deficiency in bone tissue;
- dystrophy of the cervical and spinal muscles;
- diseases of the neuromuscular system (cerebral palsy, central (spastic) paralysis, congenital syringomyelia).
 The share of congenital pathologies accounts for about 20% of all cases of the disease, the remaining 80% are acquired. And they distinguish true scoliosis and scoliotic disease... In the first case, there are persistent changes in the vertebrae, and in the second they are not, there is only muscle imbalance, which is the cause of the lateral curvature. Untreated scoliotic posture can develop into scoliosis.
The share of congenital pathologies accounts for about 20% of all cases of the disease, the remaining 80% are acquired. And they distinguish true scoliosis and scoliotic disease... In the first case, there are persistent changes in the vertebrae, and in the second they are not, there is only muscle imbalance, which is the cause of the lateral curvature. Untreated scoliotic posture can develop into scoliosis.
The reasons for acquired scoliosis include:
- prolonged stay in an unnatural position for the spine;
- carrying weights mainly in one hand;
- injuries to the legs, pelvis, spine;
- damage to the spinal column by causative agents of tuberculosis or syphilis;
- inflammation of the skeletal muscles;
- shortening of one leg.
Good to know: Predisposing factors for the development of childhood scoliosis are sports that involve asymmetric movements and playing "asymmetrical" musical instruments.
So, the risk of getting sick is higher in fencers, tennis players, boxers often have a stoop. But doing acrobatics or gymnastics can also adversely affect posture, since they develop excessive mobility of the spine. Among musicians, scoliosis is more common in children taking violin or accordion lessons than in those who play drums or keyboards.
 The spine of a newborn normally does not have any bends, it is even. Physiological curves of the back are formed at certain stages of a child's development. Flexion in the cervical spine begins from the moment when the baby learns to hold the head (approximately 3-4 months of age). When the baby learns to sit (at 6-7 months), the bend appears in the thoracic region, and with the acquisition of upright walking skills - in the lumbar and sacrococcygeal. When a child appears in a family, it is important to adhere to his individual rhythm of development, wait until he learns to sit down, crawl, get up, walk on his own, and not force events and not try to teach him to perform these actions ahead of time. Birth trauma can also be a prerequisite for poor posture. Traumatic childbirth increases the risk of malformation of the musculoskeletal system.
The spine of a newborn normally does not have any bends, it is even. Physiological curves of the back are formed at certain stages of a child's development. Flexion in the cervical spine begins from the moment when the baby learns to hold the head (approximately 3-4 months of age). When the baby learns to sit (at 6-7 months), the bend appears in the thoracic region, and with the acquisition of upright walking skills - in the lumbar and sacrococcygeal. When a child appears in a family, it is important to adhere to his individual rhythm of development, wait until he learns to sit down, crawl, get up, walk on his own, and not force events and not try to teach him to perform these actions ahead of time. Birth trauma can also be a prerequisite for poor posture. Traumatic childbirth increases the risk of malformation of the musculoskeletal system.
Good to know: the enemies of a beautiful posture are also too soft a sleeping place, tight clothes, shoes that can cause clubfoot, shoes with very high heels, poor lighting of the workplace, since you have to bend too much, the habit of lifting weights from an inclined position.
However, experts still call the main reason for the development of scoliosis the wrong posture at the table.
Types, forms and stages of the disease
As mentioned above, there are two types of scoliosis congenital (primary) and acquired (secondary).
The disease is most likely manifested at a time when the body is growing most intensively.
In this regard, there is a certain classification of scoliosis:
- infantile - occurs at the age of one to two years;
- juvenile - typical for children from four to six years old;
- adolescent (adolescent) - appears mainly between ten and fourteen years.
 Separation of scoliosis by the nature of anatomical changes:
Separation of scoliosis by the nature of anatomical changes:
- structural;
- non-structural.
Based on the magnitude of the angle of deformation, four stages of the disease are distinguished:
- the first is an angle less than 10 degrees. Since the human skeleton is not perfectly symmetrical, everyone has a slight deviation in one direction or another, therefore this stage can be considered a variant of the norm;
- the second is an angle from 10 to 25 degrees;
- the third is an angle from 25 to 50 degrees;
- the fourth - 50 degrees or more.
Curvatures in scoliosis are of several types. Depending on the number of arcs of curvature, C-shaped (one arc), S-shaped (two arcs) and E-shaped scoliosis (three arcs).
The clinical course of scoliosis can also be different: not progressive, slowly progressing, rapidly progressing.
Scoliosis symptoms
Important: you can suspect a curvature of posture in a child even before he turns a year. Children with this problem have asymmetrical folds, often tilt their heads to one side, prefer one mother's breast over another, and crawl in circles.
Poor posture causes severe stress on all parts of the musculoskeletal system and can cause pain and discomfort.
The more it progresses, the easier it is to recognize scoliosis. At the first stage, lateral deviation is almost imperceptible to the naked eye; only slight asymmetry of the shoulders - one of them is slightly lower than the other. In the second stage, it can already be seen hump in the area of \u200b\u200bthe scapula and noticeable arcs on the spine. The third stage of scoliosis has well-recognized features. At this stage, it becomes clearly clear that scoliosis is not only body asymmetry and curvature of the spinal column, but also the formation of protrusions in the area of \u200b\u200bthe shoulder blades and ribs; on the X-ray image, you can see that the vertebrae acquire a wedge-shaped shape in the places of greatest curvature. The fourth stage is characterized by disfigurement of the figure, a change in the shape of the back, the presence of anterior and posterior rib humps, deformation of the pelvis and chest is observed, which leads to compression of the lungs and heart, which affects the work of these organs, causing pain, shortness of breath.
Diagnosis of scoliosis
It is extremely difficult to determine the presence of a congenital form of scoliosis, especially if the disease is at an early stage, without special research. However, in the prone position in babies, there is an asymmetry in the natural folds, buttocks, shoulder blades, ribs or back muscles.
Important: when there is a suspicion of scoliosis in a child who already knows how to stand, then you can organize a small test for him. To do this, ask him to lean forward and lower his hands to the floor. Normally, a person easily touches the floor with his fingertips, if he can touch the floor with his palm, this may indicate hypermobility of the joints.
But when the distance from the fingers to the floor is significant, then this indicates a chronic muscle spasm. In the slope, it is also easy to notice the curvature of the ribs, a bulging shoulder blade or a skewed pelvis. The latter may also be evidence of a shortening of one of the legs.
 The next position in which you need to examine the child is standing with feet brought together and hands down, leaning against the wall with the back of the head, back, buttocks and heels. In this case, the distance from the wall to the waist and neck will be equal to the palm flat against the wall. Otherwise, the curvature is evident. A healthy child will also easily press his shoulders against the wall at the request of the parents.
The next position in which you need to examine the child is standing with feet brought together and hands down, leaning against the wall with the back of the head, back, buttocks and heels. In this case, the distance from the wall to the waist and neck will be equal to the palm flat against the wall. Otherwise, the curvature is evident. A healthy child will also easily press his shoulders against the wall at the request of the parents.
Another home diagnostic method is plumb line test... To do this, you need to attach a thread with a weight at the end to the seventh cervical vertebra (it protrudes slightly at the base of the neck). The thread should run along the spine and between the buttocks. If there are noticeable deviations and bends in one direction or another, then this is a sure sign of scoliosis.
It should be noted that if, when viewed while standing in any position, changes and deformations are noticeable, and in the prone position they disappear, then we are talking about scoliotic posture. Thus, it is possible to make a preliminary visual diagnosis even at home, but the diagnosis can only be confirmed with the help of radiography. Based on the research data, the orthopedic surgeon will determine the curvature angle, which is the main indicator for choosing a treatment method.
Scoliosis treatment
Scoliosis is curable as long as the spine continues to formtherefore, in children, it lends itself best to correction. For treatment, conservative and surgical methods are used. As a rule, a set of various measures is used, the choice of which depends on the stage of the disease.
Treatment is aimed at eliminating the curvature and the causes that caused it. To this end the muscle corset is strengthened.
The main method of therapy in this case is therapeutic exercises, which also improves respiratory function and general condition. Physical education is always used by swimming, and sometimes with the wearing of a special active-corrective corset.
At the first stage of the development of the disease, a small correction may be quite enough to cure, namely, changes in lifestyle, some symmetrical exercises and swimming. Being in the water naturally relieves the spine, and the rowing movements make all muscle groups work. Swimming also improves movement coordination. The main swimming style for scoliosis is breaststroke on the chest.
In the second stage, as a rule, therapeutic gymnastics in combination with massage procedures. They are performed sequentially, massage relaxes spasmodic muscles and tones the weak, and gymnastics consolidates the effect. Other physiotherapeutic procedures can be used to stimulate the muscles of the back (heat therapy, electrical stimulation, electrophoresis, ultrasound).
In the third stage, the most effective therapeutic method is rigid orthopedic corsets, which are made according to an individual plaster cast. But they are not worn around the clock, because the back muscles can weaken so much that they will not have a supportive effect.
Important: the normalized spine will need such support, otherwise the disease may develop again. Therefore, in combination with a corset, therapeutic exercises are prescribed.
At the same time, exercises that lead to stretching of the spine are contraindicated (hangs, turns, bends, twists).
 In advanced cases, resort to surgical intervention. To do this, metal rods are attached to the spine, designed to fix it in the correct position.
In advanced cases, resort to surgical intervention. To do this, metal rods are attached to the spine, designed to fix it in the correct position.
Preventive actions
Prevention of the congenital form of the disease should begin even before the birth of the baby. A woman who is planning a pregnancy, to reduce the risk of developing congenital bone anomalies, should start taking vitamins: B12 and folic acid.
The next stage of prevention is preparation for childbirth and their competent management. In the presence of a birth injury in the first month of life, it is highly desirable to show it to an osteopath.
From the first months, the baby needs to be taught to a healthy lifestyle. With him, you can perform simple exercises, more often be in the fresh air. To strengthen children's bones, it is very useful which is produced in the body under the influence of ultraviolet rays.
Early detection of the disease is also a means of prevention. For this purpose, the child must be shown to an orthopedist at least twice a year. In the presence of congenital pathology, visits are indicated osteopath with the same frequency.
The task of parents is to protect their child from factors that can influence the development of scoliosis, under the influence of which the load on the musculoskeletal system is distributed asymmetrically. For this purpose it is necessary:

Important: modern children spend a lot of time in front of monitors, so the latter should be positioned correctly - at their eye level, at a distance of at least 50 centimeters. A very important place is given to correct lighting; the shadow from the child's hands should not cover the text or the keyboard.
- equip a sleeping place. A baby sleeping place should not be too soft, it is advisable to buy a moderately hard orthopedic mattress.
Also remember that children should not sit without moving for more than 20 minutes, it affects the development of the stoop. To unload the spine, they are recommended to lie down on their back or stomach on a hard surface 3-4 times during the day and lie flat for 10-15 minutes.
How to define scoliosis? Healthy back. Video
Scoliosis in children is a very common pathology that occurs very often not only among school-age children, but also among preschoolers. We will consider the causes of the development of the disease, its symptoms, methods of diagnosis, treatment and prevention.
Scoliosis concept
In a healthy person, the spinal column has four natural bends in the sagittal plane: two anterior (cervical and lumbar lordosis) and two posterior (sacral and thoracic kyphosis). The vertical plane dividing the body into the right and left halves is called the sagittal plane. Perpendicular to it, the same vertical plane passing between the front and back of the body is called the frontal. 
Scoliosis is a pathological curvature of the spinal column to the left or to the right in the frontal plane, leading to further "twisting" of the vertebrae and an increase in physiological bends. The resulting compression of blood vessels and internal organs causes disruption of the cardiovascular, respiratory, urinary, nervous and other systems of the body.
It is noticed that girls suffer from scoliosis about 9 times more often than boys. According to medical statistics, almost 10% of children and adolescents have curvature of the spinal column. Therefore, children's orthopedists confidently put scoliosis in one of the first positions among all pathologies of the musculoskeletal system.

In childhood, there are two periods when there is a leap in the growth of the body: from 6 to 7 years and from 11 to 14 years. It is these age intervals that are considered periods of high risk of developing scoliosis.
 Ask your child to stand up, turn their back to you, lower their arms along their torso and not strain. If you notice that one shoulder is higher than the other, or one shoulder blade is higher than the other, or there is more distance from the arm to the body on one side of the waist than on the other, ask the child to lean forward. In this position, you can see that not all vertebrae lie on the same line. The presence of at least one of these signs is a reasonable reason to go to an appointment with a pediatric orthopedist to exclude scoliosis. With this disease, the principle operates: early treatment is a favorable outcome. The child's body is not yet fully formed, it continues to grow, so it is much easier to resist the progression of scoliosis in a child than in an adult.
Ask your child to stand up, turn their back to you, lower their arms along their torso and not strain. If you notice that one shoulder is higher than the other, or one shoulder blade is higher than the other, or there is more distance from the arm to the body on one side of the waist than on the other, ask the child to lean forward. In this position, you can see that not all vertebrae lie on the same line. The presence of at least one of these signs is a reasonable reason to go to an appointment with a pediatric orthopedist to exclude scoliosis. With this disease, the principle operates: early treatment is a favorable outcome. The child's body is not yet fully formed, it continues to grow, so it is much easier to resist the progression of scoliosis in a child than in an adult.
Classification of scoliosis
In orthopedics, various classifications of scoliosis are used depending on the reasons for their development, the severity of the pathological process, the time of manifestation of the disease, etc.
If scoliosis manifests itself between the first and second year of a child's life, it is called infantile. If the disease manifests itself at the age of 4–6 years, they speak of juvenile scoliosis, at 10–14 years of age - of adolescence.
There are two main types of scoliosis:
- Congenital scoliosis, which is formed in the prenatal period due to the abnormal development of osteochondral structures. It can be caused by:
- developmental anomalies of the spine (hemivertebrae, wedge-shaped vertebrae);
- dysplasia of the sacro-lumbar spine;
- additional ribs or fusion of ribs.
At the same time, the transitional parts of the spine (lumbar-thoracic, cervicothoracic, lumbosacral) suffer more often. But usually there is no large arch of curvature, since single vertebrae are involved in the process. Therefore, congenital scoliosis manifests itself not earlier than 5-7 years.
- Acquired scoliosis formed in a child after birth under the influence of certain factors.
Depending on the origin and the causes of the disease, there are 5 groups of scoliosis:
- Scoliosis muscular origin. They are formed due to the pathology of muscles and ligaments, for example, with muscular dystrophy, muscular hypotension, congenital dislocation of the hip, contracture of the hip or knee joint, congenital torticollis.
- Scoliosis neurogenicorigin. They develop as a result of spinal cord injury, Friedreich's ataxia, postponed poliomyelitis, cerebral palsy, syringomyelia and other pathologies of the nervous system.
- Dysplastic scoliosis is all congenital scoliosis.
- Scoliosis, which are based on injuries and diseases chest(spinal fractures, pleural empyema, extensive burns, thoracoplasty, etc.) and other pathological conditions (rickets, juvenile rheumatoid arthritis, Hunter's syndrome, Marfan's syndrome, juvenile osteochondrosis, tumors of the spinal cord and spine, etc.).
- Idiopathic scoliosis, the causes of which have not been established. This group includes most of the scoliosis developing in childhood and adolescence.
Factors contributing to scoliotic curvature of the spinal column:
- hypodynamia;
- asthenic conditions;
- not age-appropriate load on the spine;
- improper posture;
- the formation of the musculoskeletal system lasting up to 18 years.
By the shape of the curvature, scoliosis are as follows:
- C-shapedwhen the spine has one arc in the frontal plane;
- S-shaped - two arcs;
- Z-shaped - three arcs.

According to the location of the apex of the lateral curvature of the spine, several types of scoliosis are distinguished:
- cervicothoracic (at the level of III – IV thoracic vertebrae);
- thoracic (at the level of VIII – IX thoracic vertebrae);
- lumbar-thoracic (at the level of the XI-XII thoracic vertebrae);
- lumbar (at the level of I – II lumbar vertebrae);
- lumbosacral (at the level of V lumbar and I coccygeal vertebrae).
There are several different clinical and radiological classifications of scoliosis in terms of severity. Our doctors use the classification of the outstanding domestic traumatologist-orthopedist Chaklin V.D.compiled in 1973.
I power, in which the lateral curvature of the spine is noticeable in the vertical position of the body and disappears in the horizontal position. If the child is standing, asymmetry of the shoulder blades and shoulder lines or waist is visible, which depends on the localization of the curvature. The angle of scoliosis on radiographs does not exceed 10 °;
II powerwhen the lateral deformity of the spine is more pronounced, and it does not disappear in the supine position. A rib hump begins to form, a compensatory arch appears. On the side of the curvature along the spine, a muscle roller is determined. The angle of scoliosis on an x-ray is greater than 11 ° but less than 30 °;
III power, in which a significantly pronounced lateral curvature of the spinal column is combined with a formed compensatory arch. The rib hump reaches a large size, the chest is deformed. Unloading the spine has no effect. The angle of scoliosis on the radiograph is 31 ° –60 °;
IV powerwhen the angle of scoliosis exceeds 60 °. In addition to pronounced musculoskeletal deformities, there are disruptions in the work of internal organs (heart, lungs, etc.).

Depending on the nature of the course, scoliosis can be progressive and non-progressive.
Children's scoliosis symptoms
Children with grade I – II scoliosis do not present any complaints as such. But those around them always notice a lowered head, asymmetry of the back, and flattened shoulders. At III-IV degrees of deformity, the child sometimes begins to complain of back pain, shortness of breath may disturb him, he notices transient painful sensations in the heart and palpitations. Stiffness of movements increases, the child becomes inattentive, gets tired quickly. Young children may have difficulty walking, stumbling, or losing balance.
Scoliosis is not only a physical but also a cosmetic defect. Sick children can complain of a bad mood, get depressed. Their relationships with peers are broken, self-esteem falls. Therefore, parents in the first place, as well as psychologists and doctors, should help the child overcome these problems.
Doctors of all specialties who work with children know how important early diagnosis of scoliosis is. Therefore, a doctor of a children's institution, a district pediatrician, a surgeon, a pediatric neurologist, a physiotherapist, a dermatologist, etc., can suspect a deformity of the spinal column and send a patient for further examination. 
Leads a child with scoliosis or with suspicion of it is a pediatric orthopedist, and in the absence of this doctor in the clinic - a surgeon To make a diagnosis, the doctor examines the child from the back and front, from both sides, standing straight and leaning forward, as well as sitting and lying down. In the presence of signs of scoliosis (asymmetry of the back, rib hump, etc.), he determines the degree of curvature of the spinal column in degrees using a scoliosometer. If the spine is deviated from the vertical axis by more than 5–7 °, the doctor directs the patient to.
 To identify the pathology of the spinal column, X-ray is performed in the vertical and horizontal positions of the patient in two projections. The radiologist in the conclusion indicates the degree of scoliosis, determining it by the Chaklin method. To obtain more detailed information and in the absence of contraindications, X-ray tomography, MRI or CT of the spinal column, myelography are performed. During treatment, to control its effectiveness, a non-radiation method of computed optical topography is used. Children's orthopedists often use a camera at all stages of patient observation and treatment. Comparing photographs taken at different times and from different angles, the doctor can indirectly judge the course of the disease.
To identify the pathology of the spinal column, X-ray is performed in the vertical and horizontal positions of the patient in two projections. The radiologist in the conclusion indicates the degree of scoliosis, determining it by the Chaklin method. To obtain more detailed information and in the absence of contraindications, X-ray tomography, MRI or CT of the spinal column, myelography are performed. During treatment, to control its effectiveness, a non-radiation method of computed optical topography is used. Children's orthopedists often use a camera at all stages of patient observation and treatment. Comparing photographs taken at different times and from different angles, the doctor can indirectly judge the course of the disease.
If there are indications, a child with scoliosis is consulted by a gastroenterologist, cardiologist, pulmonologist, neurologist, who can prescribe additional examination (laboratory tests, ECG, ultrasound, etc.).
 The orthopedic surgeon chooses the treatment tactics for each child strictly individually. It is determined by the patient's age, the severity of scoliosis, the course of the disease (with or without progress). All methods of treating this type of deformity of the spinal column are divided into conservative and surgical.
The orthopedic surgeon chooses the treatment tactics for each child strictly individually. It is determined by the patient's age, the severity of scoliosis, the course of the disease (with or without progress). All methods of treating this type of deformity of the spinal column are divided into conservative and surgical.
Conservative treatment includes an orthopedic regimen, massage, physiotherapy procedures, physiotherapy exercises, manual therapy, and wearing a corset. The orthopedic regimen includes constant monitoring of correct posture, sleeping on a hard shield, unloading the spine with a horizontal position of the body several times a day.
If a child has grade I – II scoliosis, and the disease does not progress, all measures are taken to eliminate the causes contributing to the curvature, to organize the patient's correct motor activity and unload the spine. The main thing is to prevent the progression of the pathological process. The child is prescribed an orthopedic regimen, massage of the entire back, therapeutic exercises, swimming.
 If scoliosis of I – II degrees progresses, the orthopedist adds a special complex of physiotherapy exercises, manual therapy (soft techniques), physiotherapy (magnetotherapy, mud and hydrotherapy, CMT therapy, electromyostimulation, heat therapy, etc.) to the above appointments, wearing an orthopedic corset , correcting the position of the spinal column.
If scoliosis of I – II degrees progresses, the orthopedist adds a special complex of physiotherapy exercises, manual therapy (soft techniques), physiotherapy (magnetotherapy, mud and hydrotherapy, CMT therapy, electromyostimulation, heat therapy, etc.) to the above appointments, wearing an orthopedic corset , correcting the position of the spinal column.
If conservative treatment does not give the desired effect, and the disease progresses, if the angle of scoliosis exceeds 40 °, and the child has impaired functions of internal organs, he is indicated for surgical treatment of the disease. Doctors try to do the operation after 10, but before 14 years, since this age interval is considered optimal for its implementation.

Surgical treatment involves the implantation of special devices (distractors, endocorrectors, etc.) into the chest, which fix the spine in the maximum possible straightened state. Surgical intervention is always preceded by traction of the spinal column. Other options for surgical treatment are osteoplastic (resection of the vertebrae), mobilizing (removal of the intervertebral disc, etc.) and cosmetic (resection of the hump, angle of the scapula, etc.) operations. After any surgical intervention, the child undergoes a long course of rehabilitation therapy.
Childhood scoliosis prognosis
Scoliosis, which manifests itself in a child at the age of 10–12, is less aggressive. The disease that manifests itself before the age of 6 years usually has a progressive course, accompanied by the early development of deformity of the spinal column. It is impossible to completely cure the disease, but it is quite possible to suspend the pathological process and reduce the severity of the curvature.
Children with scoliosis are subject to long-term supervision by an orthopedist and should receive specialized treatment at least twice a year. The prognosis in terms of mobility and independence is determined by the degree of scoliosis. Sick children with mild curvatures move freely, participate in active games along with their peers. In severe scoliosis, independence may be limited due to imbalance in the body, and the child will need a cane or walker. In this case, mobility is most often also limited, especially the tilt of the trunk.
 For girls with spinal deformity, the prognosis in terms of pregnancy is quite favorable, since special sets of exercises have been developed to facilitate the bearing of a child and prepare a woman for childbirth.
For girls with spinal deformity, the prognosis in terms of pregnancy is quite favorable, since special sets of exercises have been developed to facilitate the bearing of a child and prepare a woman for childbirth.
Young men of military age suffering from scoliosis are not or are subject to conscription in the RF Armed Forces, which is determined by the severity of the deformity.
Prevention of the disease
 Scoliosis, like many diseases, is easier to prevent than to cure. No one better than the parents of a child can cope with measures to prevent the development of spinal deformities. Only parents have the ability to constantly monitor their child.
Scoliosis, like many diseases, is easier to prevent than to cure. No one better than the parents of a child can cope with measures to prevent the development of spinal deformities. Only parents have the ability to constantly monitor their child.
- at the age of one year, do not rush the child to grow: do not put him in pillows if he cannot sit on his own, and do not use a walker if the baby is not yet standing;
- enroll your son or daughter in the pool as early as possible, since swimming is the most effective sport in terms of preventing scoliosis;
- always monitor the correct posture of the child, his physical activity and motor regime;
- by personal example, teach him to do morning exercises every day;
- buy an orthopedic mattress for your child to sleep;
- properly organize his workplace, buy a satchel for the school.
Remember that in both the treatment and prevention of scoliosis, patience and persistence combined with confidence and optimism will lead you to success.
Zaluzhanskaya Elena Alexandrovna, pediatrician