Funds credited to bank deposits are reflected as part of financial investments. But provided that, according to the agreement with the company’s bank, income will be accrued on them. Otherwise, such funds are reflected in line 1250 “Cash” of the unified form of the balance sheet (account 55 “Special accounts in banks”). According to civil legislation, under a bank deposit agreement, a bank that has accepted a sum of money (deposit) received from a depositor undertakes to return it and pay interest on it under the conditions and in the manner prescribed by the agreement.
Interest on the deposit is accrued on the terms specified in the agreement on the day when the company has the right to receive it. In this case, for the purpose of reflecting accrued interest on the accounting accounts, it does not matter whether the bank credited the interest to the company’s account or not.
There is an exception to this rule. Thus, the deposit agreement may establish the dependence of the amount of interest on the term of placement of the money. And if the contract is terminated early, the interest rate is revised downward and is paid upon expiration or termination of the contract. In such a situation, interest can be reflected in accounting only after it is actually received by the company. Let's explain why. Thus, interest received for the provision of funds for use is reflected in a manner similar to that specified in paragraph 12 of PBU 9/99.
Paragraph 12 of PBU 9/99 provides that income is recognized in accounting, in particular, when the following conditions are met:
The organization has the right to receive this revenue arising from a specific contract or otherwise confirmed in an appropriate manner;
The amount of revenue can be determined;
There is confidence that a particular transaction will result in an increase in the economic benefits of the organization.
If the bank deposit agreement does not provide for the accrual of interest at the end of the reporting period, then in this case there is no certainty that as a result of this operation there will be an increase in economic benefits. In addition, it should be borne in mind that in the situation under consideration, the amount of interest may be changed. Consequently, the company cannot reliably determine the amount of interest due to it (it can only be calculated at the end of the contract or after its termination).
Example
In January, the company deposited money into a long-term bank deposit in the amount of RUB 500,000.
Situation 1
Under the terms of the agreement, the company is accrued and paid monthly interest at the rate of 9% per annum.
Debit 58 Credit 51
Debit 76 Credit 91-1
3811 rub. (RUB 500,000 x 9%: 366 days x 31 days) - interest accrued for January;
Debit 51 Credit 76
3811 rub. - interest received for January;
Debit 76 Credit 91-1
3566 rub. (RUB 500,000 x 9%: 366 days x 29 days) - interest accrued for February;
Debit 51 Credit 76
3566 rub. - interest received for February;
Debit 76 Credit 91-1
3811 rub. (RUB 500,000 x 9%: 366 days x 31 days) - interest accrued for March;
Debit 51 Credit 76
3811 rub. - interest received for March.
Debit 51 Credit 58
500,000 rub. - funds were returned from the deposit account.
Situation 2
According to the terms of the agreement, interest is accrued and paid upon expiration of its validity period at the rate of 9% per annum. In case of early termination, interest is charged at the rate of 1.5% per annum. The contract was concluded for a period of 1095 days. and was not terminated early.
Transactions for depositing funds and receiving interest are reflected in the following entries:
Debit 58 Credit 51
500,000 rub. - funds have been deposited into a bank deposit;
Debit 76 Credit 91-1
RUB 134,631 (RUB 500,000 x 9%: 366 days x 1095 days) - interest accrued on the deposit;
Debit 51 Credit 58
500,000 rub. - funds were returned from the deposit account;
Debit 51 Credit 76
RUB 134,631 - interest on the deposit was received.
Expert opinion
In tax accounting, taking into account the provisions of paragraph 6 of Article 271 of the Tax Code, under loan agreements and other similar agreements (other debt obligations, including securities), the validity of which falls on more than one reporting period, income is recognized as received and is included in corresponding income at the end of the relevant reporting period. Consequently, if a bank deposit agreement is concluded for a period of more than one reporting period, the depositor organization is obliged to accrue interest at the end of each reporting period, regardless of the actual receipt of money and the terms of the deposit agreement (provided that this organization keeps records of income and expenses for tax purposes accrual method).
O. Volkova, expert of the Legal Consulting Service GARANT
V. Gornostaev, reviewer of the Legal Consulting Service GARANT
Based on materials from the reference book "Annual Report"under general edited by V. Vereshchaki
Funds credited to bank deposits are reflected as part of financial investments. But provided that, according to the agreement with the company’s bank, income will be accrued on them. Otherwise, such funds are reflected in line 1250 “Cash” of the unified form of the balance sheet (account “Special accounts in banks”). According to civil legislation, under a bank deposit agreement, a bank that has accepted a sum of money (deposit) received from a depositor undertakes to return it and pay interest on it under the conditions and in the manner prescribed by the agreement.
Interest on the deposit is accrued on the terms specified in the agreement on the day when the company has the right to receive it. In this case, for the purpose of reflecting accrued interest on the accounting accounts, it does not matter whether the bank credited the interest to the company’s account or not.
There is an exception to this rule. Thus, the deposit agreement may establish the dependence of the amount of interest on the term of placement of the money. And if the contract is terminated early, the interest rate is revised downward and is paid upon expiration or termination of the contract. In such a situation, interest can be reflected in accounting only after it is actually received by the company. Let's explain why. Thus, interest received for the provision of funds for use is reflected in a manner similar to that specified in paragraph 12 of PBU 9/99.
Paragraph 12 of PBU 9/99 provides that income is recognized in accounting, in particular, when the following conditions are met:
The organization has the right to receive this revenue arising from a specific contract or otherwise confirmed in an appropriate manner;
The amount of revenue can be determined;
There is confidence that a particular transaction will result in an increase in the economic benefits of the organization.
If the bank deposit agreement does not provide for the accrual of interest at the end of the reporting period, then in this case there is no certainty that as a result of this operation there will be an increase in economic benefits. In addition, it should be borne in mind that in the situation under consideration, the amount of interest may be changed. Consequently, the company cannot reliably determine the amount of interest due to it (it can only be calculated at the end of the contract or after its termination).
Example
In January, the company deposited money into a long-term bank deposit in the amount of RUB 500,000.
Situation 1
Under the terms of the agreement, the company is accrued and paid monthly interest at the rate of 9% per annum.
3811 rub. (RUB 500,000 x 9%: 366 days x 31 days) - interest accrued for January;
3811 rub. - interest received for January;
3566 rub. (RUB 500,000 x 9%: 366 days x 29 days) - interest accrued for February;
3566 rub. - interest received for February;
3811 rub. (RUB 500,000 x 9%: 366 days x 31 days) - interest accrued for March;
3811 rub. - interest received for March.
500,000 rub. - funds were returned from the deposit account.
Situation 2
According to the terms of the agreement, interest is accrued and paid upon expiration of its validity period at the rate of 9% per annum. In case of early termination, interest is charged at the rate of 1.5% per annum. The contract was concluded for a period of 1095 days. and was not terminated early.
Transactions for depositing funds and receiving interest are reflected in the following entries:
500,000 rub. - funds have been deposited into a bank deposit;
Debit Credit 91-1, income is recognized as received and included in the relevant income at the end of the corresponding reporting period. Consequently, if a bank deposit agreement is concluded for a period of more than one reporting period, the depositor organization is obliged to accrue interest at the end of each reporting period, regardless of the actual receipt of money and the terms of the deposit agreement (provided that this organization also conducts expenses for tax purposes using the method accruals).
O. Volkova, expert of the Legal Consulting Service GARANT
V. Gornostaev, reviewer of the Legal Consulting Service GARANT
Based on materials from the reference book "Annual Report"
under general edited by V. Vereshchaki
The client bank where we work has added a service: deposit the amount from the account into a time deposit from 2 to 90 days. rate 6.71 We want to deposit 2,000,000 rubles for 90 days inclusive. Question: 1. How to take into account the write-off from the account to the deposit? (what transactions and on the basis of what documents to do this) 2. How to take into account the receipt (at the end of 90 days) of funds and interest on them. 3. Will the received interest be considered income and taken into account when calculating income tax (in income). 4. And is there a difference in the period in which we deposit the money, i.e. in one reporting period, for example, from July 1, 2013 to September 28, 2013 (Q3), or can we deposit from June 1 to August 28 in different reporting periods (2-3 quarter)? or does it not matter, because the income will still rise in the 3rd quarter? and so and so. 5. And how risky this procedure is during tax inspections. How to properly arrange and record all this (postings).
There is no need to report the opening of a deposit in a bank to either the tax office or the funds.
Accounting
In accounting, reflect the deposit amount on account 55 of the “Deposit Accounts” subaccount or on account 58. The organization chooses the accounting methodology independently, having established this in the accounting policy.
The following transactions are reflected in accounting:
Debit 55-3 (58) Credit 51
Debit 76 Credit 91-1
Debit 55-3 (58) Credit 76
Debit 51 Credit 55-3 (58)
In accounting, deposit interest is recognized as income on the last day of each month.
Tax accounting
Income (interest) on the deposit deposit should be included in non-operating income (clause 6 of Article 250 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) on the last day of the month or on the date of termination of the bank deposit agreement (clause 6 of Article 271, paragraph 2 of clause 4 of Art. 328 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Establish a specific methodology in your accounting policy for tax purposes.
To avoid differences between accounting and tax accounting, recognize income on the deposit at the end of each month.
Documenting
The documents used to formalize transactions for placing and returning a deposit are:
1. Agreement with the bank (is the main document for recording the amount of the deposit, as well as interest on it);
2. Bank statement for the deposit account;
3. Accounting certificate (serves to reflect interest accrual transactions in accounting and tax accounting)
As for the period for which the deposit will be opened, your organization sets it independently; this does not entail any tax consequences.
The rationale for this position is given below in the materials of the Glavbukh System vip version
To carry out certain operations, organizations on their own initiative can open special accounts in banks (Article 30 of the Law of December 2, 1990 No. 395-1, clauses 2.1 and 2.8 of the Bank of Russia Instruction of September 14, 2006 No. 28-I).
Funds are credited to special accounts from settlement or foreign currency accounts of organizations. Also, the source of funds in a special account can be a loan provided by the bank.
Opening special accounts
Typically, special bank accounts are opened:
· for settlements under letters of credit;
· for payments by checks;
· for accounting of deposits (deposits);
· for payments using bank cards.*
In addition, on their own initiative, banks open to organizations:
· loan accounts – for the movement of funds provided under loan agreements;
· transit currency accounts – to record receipts in foreign currency. Regardless of the organization’s wishes, a transit currency account is opened simultaneously with a current currency account.
A special account can be opened both in rubles and in foreign currency. To do this, you need to submit an application to the bank (in a form approved by the bank) and attach a payment order for the transfer of funds.
Report to the inspectorate and funds
The organization must inform about the opening of a special account for payments by bank cards:
· to the tax office at the place of your registration;
· to the territorial branches of the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation and the Social Insurance Fund of Russia.
This must be done within seven working days from the date of opening (closing) the account. This is stated in subparagraph 1 of paragraph 2 of Article 23 and paragraph 6 of Article 6.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, as well as paragraph 1 of part 3 of Article 28, part 6 of Article 4 and part 1 of Article 3 of the Law of July 24, 2009 No. 212-FZ.
A complete list of bank accounts, the opening of which must be reported to the regulatory authorities (tax inspectorate, Pension Fund of the Russian Federation and Social Insurance Fund of Russia), is given in the table.
The Pension Fund of the Russian Federation recommends using the form for reporting, which is posted on the official website of the fund in the “Recommended sample documents” section. To send a message to the FSS of Russia, you can use the form recommended in the letter of the FSS of Russia dated December 28, 2009 No. 02-10/05-13656.
Attention: for violation of the deadline for providing information on opening (closing) a bank account to state extra-budgetary funds, liability is provided. The fine for an organization will be 5,000 rubles, and for its officials, for example a manager, from 1,000 to 2,000 rubles. This is stated in Part 1 of Article 15.33 of the Code of the Russian Federation on Administrative Offenses and Article 46.1 of the Law of July 24, 2009 No. 212-FZ.
Accounting: special accounts
In accounting, reflect the movement of money in special accounts on account 55 “Special accounts in banks.” The following sub-accounts can be opened for account 55:*
· 55-1 “Letters of credit”;
· 55-2 “Checkbooks”;
· 55-3 “Deposit accounts”;*
· 55-4 “Special card account”, etc.
Accounting for the availability and movement of funds in rubles and foreign currencies should be kept in different sub-accounts opened for account 55 (for example, in the sub-accounts “Special card account in rubles”, “Special card account in foreign currency”).
Funds in special accounts in foreign currency are converted into rubles at the Bank of Russia exchange rate on the date of transactions in foreign currency, as well as on the reporting date (clauses 4–7 of PBU 3/2006). Positive exchange differences arising in this case are included in other income (clause 7 of PBU 9/99), negative ones - in other expenses (clause 11 of PBU 10/99).
Loan and transit currency accounts are internal accounts of banks and are opened by them for control functions. In the accounting of organizations, transactions carried out on them are not reflected in account 55. To record debt on loan accounts, use accounts 66 and 67. To reflect transactions on the transit currency account to account 52, you can open a separate subaccount of the same name.
Deposit account
If an organization has available funds and intends to receive income from placing them in a bank, then a special deposit account is opened for it, on which the bank will accrue interest monthly. The bank opens such an account on the basis of a bank deposit agreement (Articles 834, 835 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation), which stipulates:
· type of deposit;
· the amount that is deposited or transferred to the deposit;
· the amount of the deposit account maintenance fee;
· shelf life;
· responsibility of the parties;
· conditions for termination of the contract;
· other conditions as agreed by the parties.
After the deposit period expires, the bank will return the money from the special account to the organization’s current account.
In accounting, the movement of money in deposits is reflected in account 55-3 “Deposit accounts in banks.”
Reflect the transfer of funds to the deposit by posting:
Debit 55-3 Credit 51 (52)
– funds are transferred to a special deposit account.
When the bank returns the deposit amount, make a reverse entry.
When calculating and paying interest on a deposit, make the following entries in your accounting:
Debit 76 Credit 91-1
– interest accrued on the deposit;
Debit 51 Credit 76
– interest on the deposit is credited to the current account.
The bank deposit agreement may provide for the payment of the entire amount of interest on the deposit upon expiration of the period of storage of funds on deposit. In this case, interest accumulates in the deposit account during the entire period of storage of the money, and then the bank transfers it to the settlement (currency) account of the organization. Reflect such transactions in accounting with the following entries:
Debit 55-3 Credit 76
– interest on the deposit is credited to the deposit account;
Debit 51 (52) Credit 55-3
– interest on the deposit is credited to the current (currency) account.
Analytical accounting for account 55-3 “Deposit accounts” is maintained for each deposit separately.
Since deposits are recognized as financial investments (clause 3 of PBU 19/02), they can be accounted for in account 58 “Financial investments”. The organization establishes the method of accounting for the movement of money on deposit in its accounting policy.
Oleg Horoshiy,
Income (interest) on deposits should be included in non-operating income (clause 6 of Article 250 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
· with the accrual method - on the last day of the month or on the date of termination of the bank deposit agreement (clause 6 of article 271, paragraph 2 of clause 4 of article 328 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
· with the cash method - on the day the funds are received into the bank account (clause 2 of Article 273 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Oleg Horoshiy,
State Advisor to the Tax Service of the Russian Federation, III rank
3. Table:List of bank (personal) accounts, the opening (closing) of which must be reported to regulatory authorities
|
Account type |
Reason for opening an account |
Ability to spend money |
Is it necessary to inform the regulatory authorities (tax office, Pension Fund of the Russian Federation, Social Insurance Fund of Russia) about the account? |
|
Savings account |
No contract |
||
|
Checking account |
Bank account agreement |
||
|
Current currency account |
Bank account agreement |
||
|
Transit currency account |
Bank account agreement |
||
|
Special currency account |
Bank account agreement |
||
|
Loan account |
Loan agreement |
||
|
Deposit account* |
Bank deposit agreement |
||
|
Special card account |
Bank account agreement |
||
|
Bank account abroad |
Bank account agreement |
||
|
Personal account |
Constituent documents |
You need to go to the tax office The Pension Fund of the Russian Federation and the Social Insurance Fund of Russia are not required** |
|
|
Brokerage account opened for conducting settlements on transactions with securities and other related operations |
Bank account agreement |
||
|
Current account of an individual |
Bank account agreement |
* The procedure for spending budget funds from personal accounts opened in territorial divisions of the Federal Treasury is regulated by budget legislation.
** Information on the opening (closing) of personal accounts opened with territorial bodies of the Federal Treasury (financial authorities) is provided only to the tax office at the place of registration (subclause 1, clause 2, article 23 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The obligation to provide such information to the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation, the Social Insurance Fund of Russia is not established by Law No. 212-FZ of July 24, 2009.
*** The broker has the right to spend funds in a special brokerage account under the terms of the brokerage service agreement (clause 3 of article 3 of the Law of April 22, 1996 No. 39-FZ).
**** Information on the use by entrepreneurs of personal accounts of individuals for settlements related to business activities is provided at the place of registration to the tax office, the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation and the Social Insurance Fund of Russia (subclause 1, clause 2, article 23 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, subclause 1 Part 3 of Article 28 of the Law of July 24, 2009 No. 212-FZ, letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated March 6, 2013 No. ED-3-3/772).
From a legal point of view, we will talk about a bank deposit, the rules of which are established by the 44th chapter of the same name of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
There is a well-known contradiction regarding the accounting of deposits in the accounting regulatory framework. According to the Instructions for the Application of the Chart of Accounts (hereinafter referred to as the Chart of Accounts), the presence and movement of deposits is taken into account in subaccount 55.3 “Deposit accounts” of account 55 “Special accounts in banks”; on the other hand, according to paragraph 3 of PBU 19/02 “Accounting for financial investments”, deposits in credit institutions are classified as financial investments:
However, the IPPS does not directly provide for taking into account bank deposits in a special account 58 “Financial Investments”, therefore, without going further into theoretical reasoning, we will use account 55.03 “Deposit Accounts” to record deposits. At the same time, it is possible to use account 58 instead - this will not significantly affect the procedure for processing bank deposit transactions in 1C Accounting. In general, the specific method of accounting for deposits in an organization is established by the accounting policy.
Making a deposit in 1C 8.3 Accounting
Let's assume the following business situation:
01/25/2016 Our organization entered into a bank deposit agreement and deposited 1,000,000 rubles into the deposit account. for a period of 6 months at 12% per annum. The agreement provides for monthly accrual and payment of interest.
Thus, in our example the postings will be involved:
- Debit 55.03 - Credit 51: transfer of funds from the organization to deposit;
- Debit 51 - Credit 55.03: the reverse entry to the previous one, that is, the bank’s return of invested funds.
Note: if the deposit is opened in foreign currency, then account 52 “Currency accounts” corresponds with the account for accounting for financial investments.
- Debit 76 - Credit 91.1: accrual of incoming interest on the deposit;
- Debit 51 - Credit 76: payment of interest on the deposit.
The example uses a demo base based on the Enterprise Accounting configuration, edition 3.0 (3.0.43.241).
Transfer of funds to a deposit in 1C 8.3
To formalize the transaction of transferring funds from the organization’s current account to a bank deposit in 1C Accounting 3.0, the document “ “ is used. To create it, let's turn to the Bank Statements journal in the Bank and Cash Department - command group Bank - Bank Statements command:

At the top of the form of this journal there are buttons for manual (Receipt and Write-off) and automated (Upload - starts processing the exchange of documents with the bank) input of bank documents:

Let's manually create the document Write-off from the current account. Accordingly, by clicking the Write-off button, a new document form will open, all the necessary details of which must be filled out:
- First, you need to select the appropriate Operation Type - in our case it will be Other write-off.
- Next, in addition to the basic standard details, the debit account is indicated - 55.03, and the corresponding analytics are also filled in in the form of a bank account and.
- At the same time, the need to indicate the type of SDDS for each specific monetary transaction is established by the organization in accordance with the accounting regulatory framework.

At the output we have the expected posting, reflecting the transfer of funds to the deposit (the Show movements button):

Accrual and receipt of interest on deposits in 1C 8.3
In accounting, in accordance with paragraph 7 of PBU 9/99, interest on a deposit is recognized as other income. In tax accounting, interest on deposits is classified as non-operating income (clause 6 of Article 250 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) and is recognized as received and included in the corresponding income at the end of each month, regardless of the date of their payment (clause 6 of Article 271 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Therefore, in this general case, there will be no discrepancies in the reflection of deposit interest between these two types of accounting.
Provided that the amount of the bank deposit was received by the bank on January 25, 2016. and returned by the bank on June 24, 2016, the distribution of accrued interest by month will be calculated as follows:

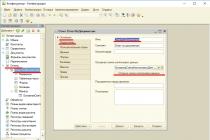
The registration of the operation of calculating interest on a bank deposit in the 1C Enterprise Accounting 8.3 program is carried out using a special document Operation. Its creation occurs from the corresponding list: section Operations - group of commands Accounting - command Operations entered manually:

In the header of the document (the upper non-tabular part) the general details for transactions (if there are several) are filled in.
To add a transaction to the tabular part of the document:
- Click the Add button;
- We fill out the necessary debit and credit accounts, as well as their analytics;
- We indicate the amount. When filling out this field in 1C 8.3, the document header details “Transaction Amount” will be automatically filled in. When the field value is changed or a new line is added, the “Transaction Amount” attribute will be automatically recalculated.
The document Operation in 1C 8.3 generates accounting entries directly:

Next, it is necessary to take into account in 1C Accounting 3.0 (8.3) the actual payment by the bank of interest on the deposit. The document Receipt to current account is suitable for this purpose. Let's create it by clicking on the button Receipt of the journal of bank statements (see above for how to get there), and fill in the details of the new document form that opens:
- First, you need to select the appropriate type of operation - in our case, Other receipt is suitable.
- Further, in addition to the basic standard details, the loan account is indicated - 76.03.
- The corresponding analytics are also filled in in the form of a counterparty, agreement and cash flow item. At the same time, the need to indicate the type of SDDS for each specific monetary transaction is established by the organization in accordance with the accounting regulatory framework:

At the output we have the expected posting, reflecting the receipt of interest on the deposit to the current account:

The above operations of accrual and receipt of interest on the deposit must be carried out in the 1C 8.3 Accounting 3.0 program on a monthly basis according to the contract schedule:

Return of deposit in 1C 8.3
So, at the end of the term of the bank deposit agreement, the bank transferred funds from the deposit account to the organization’s current account, that is, returned the money deposited.
This operation is formalized in 1C Accounting 3.0 on the basis of a bank statement confirming this fact using the document Receipt to current account already mentioned above:
- We indicate the type of operation Other receipt;
- Loan account – 55.03;
- Next, fill in the necessary analytics for the accounting accounts:

Result of the document:

We will generate reports for verification in the 1C 8.3 program: Turnover balance sheet for accounts 55.03 and 76 for the period of settlement of the deposit and at monthly intervals:

Finally…
As you can see, the Enterprise Accounting 3.0 configuration on the 1C Enterprise 8.3 platform helps the accountant simply and accurately keep records of transactions under the deposit agreement. Of course, with the help of this program you can easily and effectively solve the entire range of accounting problems, including such more rare and “tricky” situations as, for example, accounting in foreign currency,
A deposit is funds in the currency of the Russian Federation or foreign currency, placed on a repayable basis by individuals for the purpose of storing and receiving income, on the basis of a bank deposit agreement or a bank account agreement, including capitalized (accrued) interest on the deposit amount.
Income on the deposit is paid in cash in the form of interest. The deposit is returned to the depositor upon his first request in the manner prescribed for a deposit of this type by federal law and the relevant agreement.
Deposits can be accepted by banks that have an appropriate license issued by the Bank of Russia and participate in the system of compulsory insurance of individuals' deposits in banks. Participation in the deposit insurance system in accordance with the Federal Law of December 23, 2003. No. 177-FZ “On insurance of deposits of individuals in banks of the Russian Federation” is mandatory for all banks.
Bank depositors can be citizens of the Russian Federation, foreign citizens and stateless persons, in addition, minors aged 14 to 18 years have the right to independently, without the consent of parents, adoptive parents and trustees, make deposits in credit institutions and dispose of them.
Depositors can have an unlimited number of deposits in one or more banks and manage their deposits, as well as receive income and make non-cash payments in accordance with the deposit agreement.
Bank agreement with depositor
When funds are received into a deposit or deposit, an agreement is concluded with the depositor. The agreement is drawn up in writing in two copies, one of which is issued to the client. Depending on the duration of the agreements, the amount of deposits and the conditions for their return, the bank can differentiate its interest rates.
At the same time, it must indicate and agree on the procedure for paying interest on the deposit (with capitalization, without capitalization) and terms (day, month, quarter, year.). In the absence of these conditions in the agreement, interest is paid quarterly, and unpaid interest increases the amount of the deposit (capitalization), on which interest is then charged.
Cash deposits can be accepted on the terms of issuing the deposit on demand (demand deposit) or on the terms of returning the deposit after the expiration of a period specified in the agreement (time deposit). However, under a bank deposit agreement of any type, the bank is obliged to issue the deposit amount or part thereof upon the first request of the depositor. Moreover, this rule is imperative, i.e. the condition of the agreement on the citizen’s renunciation of the right to receive a deposit upon first demand is void.
The conclusion of a bank deposit agreement with a citizen and the deposit of funds by him can be certified by a savings book. A savings book is one of the forms of a bank deposit agreement. The peculiarity of registering a deposit in the form of a savings book lies, first of all, in the fact that this form is characteristic of the relationship between the depositor - a citizen and the bank. A savings book can be either registered or bearer, and a bearer savings book is a security. Both types of savings books must contain information about the bank and the status of the deposit. A registered savings book is essentially a document certifying the conclusion of a bank deposit agreement and the deposit of funds into deposits.
The absence of a personal savings book when the client appears at the bank is not an obstacle to the disposal of the deposit, since the binding legal relationship between the depositor and the bank arises from the bank deposit agreement signed by the parties. A registered savings book in case of its loss or damage can be replaced by the depositor upon his application. A bearer savings book is a security, a document certifying property rights, the exercise or transfer of which is possible only with its bearer (Article 142 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
A bearer savings book must not only formalize the citizen’s deposit of funds into a deposit account in a bank, but also certify all his rights as a depositor. Therefore, no other document than a bearer savings book can serve as a basis for the bank to issue a deposit, pay interest and execute other orders of the depositor. If the bank loses it, the bearer savings book cannot be replaced. Since the savings book is kept by the depositor, the deposit data indicated in it may not reflect the true state of the deposit (for example, in the case of replenishment of the deposit by a third party, interest accrual, etc.).
If entries are made in the personal account that are not in the savings book, when the depositor visits the bank, corresponding entries are made in his deposit book. Entries in the savings book reflect all incoming and outgoing transactions on the deposit (deposit), after each entry the balance of the deposit is displayed.
All entries in the savings book are certified by authorized bank employees. The data reflected in the savings book is the basis for settlements between the bank and the depositor, unless proven otherwise.
A personal account is opened for each depositor for each type of deposit. When performing transactions on a deposit account, it is mandatory to check the compliance of the signatures on the account documents with the depositor’s sample signature.
Accounting entries
Accounting for deposits of individuals is kept in passive account 423 “Deposits and other funds raised by individuals.” In the context of this account, balance sheet accounts of the second order are maintained according to the timing of raising funds:
- poste restante;
- for up to 30 days;
- for a period from 31 to 90 days;
- for a period from 91 to 180 days;
- for a period from 181 to 1 year;
- for a period from 1 year to 3 years;
- for a period of more than 3 years.
The opening of a deposit account for an individual is formalized by posting:
- Dt 20202 “Cash desk of credit institutions”
- Kt 423 “Deposits and other funds raised from individuals” - for the amount of the deposit received at the bank’s cash desk.
The return of the deposit amount is processed by reverse posting:
- Dt 423 “Deposits and other funds raised from individuals”
- Kt 20202 “Cash desk of credit organizations” - for the amount of the deposit paid from the bank’s cash desk.
When the deposit is returned, all interest accrued up to that time is paid.
In cases where a time deposit or another deposit, other than a demand deposit, is returned to the depositor upon his request before the expiration of the term or before the occurrence of other circumstances specified in the bank deposit agreement, interest on the deposit is paid in an amount corresponding to the amount of interest paid by the bank on demand deposits, or the bank has the right to provide in the agreement a reduced interest rate on deposits withdrawn ahead of schedule.
The bank is obliged to charge interest on the deposit amount, the amount and procedure for calculation of which are determined in the agreement for the relevant deposit. If there is no condition in the agreement on the amount of interest to be paid, the bank is obliged to pay interest in the amount of the bank interest rate (refinancing rate) on the day of payment (clause 1 of Article 838 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
The bank may provide in the agreement the right to unilaterally change the interest rate on demand deposits. Moreover, in the event of a reduction in the amount of interest, the new amount of interest is applied to deposits made by the depositor after a month from the date of notification, unless otherwise provided by the agreement. The form of the message is not regulated. These may be announcements in the media or on the premises of the bank, etc. The method of notifying the depositor may be specified in the agreement.
For deposits made by individuals, on the terms of its issuance after a certain period or upon the occurrence of circumstances stipulated by the agreement, that is, “time deposits”, the amount of interest on the deposit determined by the bank deposit agreement cannot be unilaterally reduced by the bank, unless otherwise provided by law .
Interest on the amount of a bank deposit is accrued from the day following the day it was received by the bank until the day before it is returned to the depositor or written off from the depositor’s account on other grounds (clause 1 of Article 839 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
Unless otherwise provided by the bank deposit agreement, interest on the amount of the bank deposit is paid to the depositor upon his request at the end of each quarter separately from the deposit amount, and interest not claimed within this period increases the amount of the deposit on which interest is accrued.
Accrued interest must be reflected in the bank's accounting records at least once a month and no later than the last working day of the reporting month. Interest on attracted and placed funds is accrued by the bank on the balance of the principal debt accounted for in the corresponding personal account at the beginning of the operating day.
In this case, interest accrued for the last calendar days of the reporting month, falling on non-working days, must be reflected in the corresponding accounting accounts in the bank’s balance sheet on the first day of the month following the reporting one.
Accounting entries for reflecting on the corresponding separate personal accounts the amounts due for payment (receipt) of interest must be made either on the last working day of the reporting month (in this case, interest for the last weekend days of the reporting month is accrued on the balance of the corresponding account at the end of the last working day of the reporting month ), or on the first working day of the month following the reporting one (directly when forming the balance on the 1st day of the month following the reporting one). The choice of the day on which the corresponding accounting entries are made is determined in accordance with the Bank's Accounting Policy.
Current interest accrued and paid on deposits within one month is recorded using the following entries:
- Dt 70606 “Expenses”
- Kt 423 “Deposits and other funds raised by individuals” - for the amount of interest paid by adding to the principal amount of the deposit;
- Kt 20202 “Cash desk of credit institutions”, 20207 “Cash in operating cash desks located outside the premises of credit institutions - when paying interest through the cash desk.
Reflection of accrued interest in the event that the start date of the interest accrual period and the date of payment of accrued interest fall on different months or if interest is not added to the deposit is recorded by posting:
- Dt 70606 “Expenses”
- Kt 47411 “Accrued interest on deposits” - for the amount of accrued interest.
The actual payment of interest by the borrower bank without violating the deadlines is accompanied by the following records:
- Dt 47411 “Accrued interest on deposits”
- Kt 423 “Deposits and other funds raised from individuals” – crediting accrued interest to accounts for recording deposits of individuals.
- Dt 423 “Deposits and other funds raised by individuals”
- Kt 20202 “Cash desk of credit organizations”, 20207 “Cash in operating cash desks located outside banks” - cash payment through the bank’s cash desk.
If the interest rate accrued on deposits (except for time pension deposits made for a period of at least six months) exceeds the refinancing rate of the Bank of Russia, and on deposits in foreign currency - 9%, then in part of the excess the amount is subject to income tax individuals. The tax rate for resident individuals is 35%, for non-residents – 30%.
The bank's obligation to withhold personal income tax from the amounts of accrued interest on deposits does not arise until the individual first applies to the deposit. The date of receipt of income in a calendar year is the date of payment of income (including advance payments) to an individual, or the date of transfer of income to an individual.