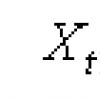Choose one correct answer:
Of the listed elements in living cells, the largest amount is present:
a) magnesium; b) nitrogen; c) phosphorus;G)carbon.
The tertiary structure of transport proteins and enzymes in the process of performing their functions:
a) does not change; b) changes;v)negoes into the secondary structure;d) goes into a quaternary structure.
With protein denaturationnot happening
destroying them:
a)primary structure;b) secondarystructures; c) tertiary structure;
d) quaternary structure.
Polymers include:
a) cellulose, sucrose, starch;b) inulin, glycogen, ribose;v)starch, inulin, cellulose;d) keratin, lecithin, fructose.
MRNA function:
a) is a part of ribosomes; b) transfers amino acids; c) storage of hereditary information; G)code transferhereditary information about the primary structure of the protein.
ATP is an important molecule in metabolism because:
a)it contains high-energy phosphate bonds;+
b) its phosphate bonds are very easily formed, but not easily broken;
c) it can be quickly obtained from the environment surrounding the body;
d) it is extremely stable.
Protein found in feathers, hair, horns, nails:
a) actin;b)keratin;+
c) tubulin;d) myosin.
Of the following mineral elementsis not essential for plants:a) potassium; b) magnesium; c) calcium;G)lead.
Mushroom Reserve Nutrient Iappears:
a) starch;b)glycogen; c) inulin;d) cellulose.
Poorly water-soluble substance:
a)heparin;b) glucose;c) vitamin C;d) mineral salts.
11. What substance is hydrophilic:
a) lipid; b) cellulose;v)sucrose; d) chitin.
12 ... Organic substances that ensure the storage of hereditary information are:
a) proteins; b) fats; c) carbohydrates;G)nucleic acids.
13 ... Hydrolysis of starch to glucose carries out:
a) pepsin;b)amylase; c) lipase; d) trypsin.
14 ... What substance is shown in the picture?
a) DNA, b) RNA,v)ATP, d) protein
15. Proteins capable of accelerating chemical reactions perform the function in the cell:
a) hormonal; b) signal;v)enzymatic; d) informational.
16. For a piece of DNAACCGATTGG indicate the complementary strand:
a) AAGGTSAGT;b)ТГГЦТААЦЦ; ТГГЦТААЦЦ; c) TCTSGTTATSG; d) TGGZATTATS.
17. Hydrolysis of fats to fatty acids and glycerin carries out:
a) pepsin; b) amylase;v)lipase; d) trypsin.
18. Indicate a pair of complementary nucleotides in a DNA molecule:
a) A = G;b)A = T; c) A = Y; d) A = C.
a) mushrooms;b)viruses; c) bacteria; d) plants.
20. Select disaccharide:
a)sucrose; b) ribose; c) glucose; d) starch.
Please select a few O option ov the answer :
The source of energy for metabolism can be:
a)proteins;+
b)fats; +
c) fat-soluble vitamins;G)carbohydrates; +
e) mineral salts; f) water.
Phosphoric acid is a part of substances:
a)DNA; b) proteins;v)RNA; d) amino acids; e) carbohydrates;e)ATP.
Polysaccharides are:
a)glycogen; b) sucrose;v)cellulose;G)murein; e) maltose; f) fructose.
Lipids in living organisms play a role:
a) enzymatic;b)reserve;v)structural;G)protective; e) receptor; f) motor.
The nucleotide contains:
a)remainder phosphoric acid; b) amino acids; c) lipids; d) enzymes;
e)a carbohydrate of ribose or deoxyribose;e)nitrogenous base.
Please select with one answer from four possible, but requiring pre-multiple choice:
Compared with the extracellular environment, the concentration of ions in the cytoplasm of the neuron is increased -I) sodium,II) potassium,III) calcium,IV) chlorine,V) magnesium.
a)I,
II;
b)I,
IV;
v)II,
V;
G)II,
III.
DNA in eukaryotic cells is in -I) cytoplasm,II) the kernel,III) mitochondria,
IV) lysosomes,V) ribosomes:
a)I,
II,
III,
V; b)I,
II,
IV;
v)II,
III; G)II,
V.
As a transport form of carbohydrates, living organisms use:
I) starch,II) glucose,III) glycogen,IV) sucrose,V) maltose.
a)II,
V;
b)I,
IV;
v)II,
IV;
G)II,
V.
4. In living organisms, the transport function is performed by proteins:
I) hemoglobin,II) hemocyanin,III) catalase,IV) globulins,V) elastin.
a)I, II, III, V; b)I, II, IV; v)II, III; G)II, V.
Compare the names of proteins (A – E) with their functions in the human body (1–5).
Protein
A. Trypsin
B. Myosin
B. Hemoglobin
G. Keratin
D. Antibodies
Function
1. Structural
2. Catalytic
3. Protective
4. Motor
5. Transport
Function
1
2
3
4
5
Protein
GG
AA
DD
BB
VV
Establish a correspondence between the characteristics of carbohydrate molecules and their types:
Features of molecules
Types of carbohydrates
1. Monomer
A- cellulose
2. Polymer
3. Dissolve in water
B- glucose
4. Do not dissolve in water
5.Is part of cell walls plants
6. Is part of cell juice
Features of molecules
1
2
3
4
5
6
Types of carbohydrates
BG
AA
BD
AB
AV
A judgment is given, with each of which one must either agree or reject.
Organogenic chemicals are:O, C, H, N. +
The DNA contains a nitrogenous base, ribose sugar, and a phosphoric acid residue. -
The monomers of DNA and RNA are nucleotides.+
Amino acid protein monomers.+
Lipids in relation to water are hydrophilic substances.-
When 1 g of fat is broken down, an energy of 17.6 kJ is released.-
Magnesium is part of chlorophyll.+
Most enzymes are proteins.+
RNA is a double unbranched linear polymer.-
Sucrose refers to disaccharides, it is found only in plants, where it is the main transported substance.+
1.What is the name of a large group of fat-like substances insoluble in water:
A) lipids;
B) proteins;
C) enzymes;
D) hormones.
2. Name the protein monomer:
A) glycerin;
B) amino acid;
C) glucose;
D) nucleotide.
3.How many hydrogen bonds are formed between adenine and thymine:
A) three;
B) two;
B) one;
D) four.
4.RNA monomer is:
A) glucose;
B) amino acid;
B) glycerin;
D) nucleotide.
5.How are the bonds between the residues of phosphoric acid ATP called:
A) macroergic;
B) energy;
B) phosphoric;
D) adenosine triphosphate.
6. Substances that change the rate of a chemical reaction, but are not part of the reaction products, are called:
A) polysaccharides;
B) polymers;
B) catalysts;
D) monomers.
7.Polysaccharides do not include:
A) glycogen;
B) fructose;
B) cellulose;
D) starch.
8. What is the name of the non-protein compound that is part of the enzymes:
A) capsid;
B) catalyst;
C) coenzyme;
D) protein.
9.The composition of fats includes:
A) nucleotide;
B) amino acid;
C) glucose;
D) glycerin.
10.RNA does not include:
A) adenine;
B) thymine;
C) cytosine;
D) uracil.
11. In the cell, lipids perform the function:
A) energy;
B) informational;
B) catalytic.
D) motor.
12. The coiled polypeptide chain is the structure of the protein:
A) primary;
B) secondary;
B) tertiary.
D) quaternary.
13. Establish a correspondence between the classes of organic substances and their functions:
Squirrels
Nucleic acids
Carbohydrates
lipids
Functions:
A) regulatory;
B) storage and transmission of hereditary information;
B) energy;
D) construction;
D) storing;
E) catalytic;
G) protective;
H) signal;
I) motor.
14. Establish a correspondence between the classes of organic substances and their representatives:
carbohydrates;
lipids;
proteins.
Representatives:
A) wax;
B) hemoglobin;
B) starch;
D) antibodies;
E) fats;
E) fructose.
15. Establish a correspondence between views nucleic acids and their signs:
DNA;
RNA.
A) the molecule is a double helix;
B) consists of one chain of monomers;
C) the composition of nucleotides includes nitrogenous bases A, C, G, U.
D) the composition of nucleotides includes nitrogenous bases A, C, G, T.
E) there is a principle of complementarity in the structure;
E) different types are distinguished, depending on the function performed.
G) the composition includes ribose;
H) the composition includes deoxyribose.
16. From the following carbohydrates, select monosaccharides:
Ribose;
Glycogen;
Cellulose;
Fructose;
Starch;
Glucose.
17. Which of the listed substances are not polymers:
Glucose;
DNA;
Hemoglobin;
Fructose;
tRNA;
Ribose.
18. Establish the sequence of complication of the structure of the protein molecule:
A) several linked protein globules;
B) the sequence of amino acids in the polypeptide chain;
C) a polypeptide chain twisted into a spiral;
D) three-dimensional spatial "packing" of the polypeptide chain.
19. Find errors in the text provided, indicate the numbers of the proposals in which they were made, correct the errors:
Viruses have a cellular structure.
The protein coat of viruses is called a capsid.
Viruses are made up of carbohydrates and lipids.
Tuberculosis is a viral disease.
Viruses can cause disease not only in animals but also in plants.
20. Given a fragment of one DNA strand: A-G-T-T-T-C-G-A-A-C-G-. Build a complementary second strand.
21. Find errors in the DNA molecule:
A-G-A-T-T-C-C-A-T-G-
T-G-T-A-T-G-T-A-T-
22. Find errors in the RNA molecule: A-A-T-G-C-U-T-A-T-C.
Answers:
1a; 2b; 3b; 4d; 5a; 6c; 7b; 8c; 9g; 10b; 11a; 12c.
1- a, c, d, f, g, h, and
2 - b
3 - c, d, e
4 - c, d, e, f
14.1-B, E
2-A, D
3-B, D
1 - A, D, D, Z
2 - B, C, E, G.
16. 1,4,6
17. 1,4,6
18. B.V.G.A.
1 - viruses do not have a cellular structure;
4 - viruses consist of a nucleic acid and a protein coat;
5 - tuberculosis is a bacterial disease.
20.A-G-T-T-T-C-G-A-A-C-G
T-C-A-A-A-G-C-T-T-G-C
21. Find errors in the DNA molecule:
A-G-A-T-T-C-C-A-T-G-
T-G-T-A-T-G-T-A-T-the principle of complementarity is violated: AT; C-G.
22. Find errors in the RNA molecule: A-A-T-G-C-U-T-A-T-C. - in the RNA molecule there is no nitrogenous base of thymine, it is replaced by uracil.
Grade 9
Option 1
A) polymer
B) homopolymer
2. Which of the following substances NOT are polymers?
A) glucose B) cholesterol
B) glycogen D) hemoglobin
3. Select polysaccharides from the following:
A) glucose E) sucrose
B) starch G) chitin
C) ribose H) lactose
D) glycogen I) fructose
E) deoxyribose K) cellulose
4. Protein monomer is:
A) nucleotide
B) amino acid
C) glucose
D) glycerin
5. The starch monomer is:
A) nucleotide
B) amino acid
C) glucose
D) glycerin
6. Proteins that regulate the rate and direction of chemical reactions in the cell:
A) hormones
B) enzymes
B) vitamins
D) proteins
7. The sequence of monomers in a polymer is called:
A) primary structure
B) secondary structure
B) tertiary structure
D) quaternary structure
Substances: Functions:
1.energy
2.structural
A) lipids 3. stock nutrients
4.protective
5.information
6.catalytic
7.transport
Grade 9
Independent work on the topic:
« Molecular level organizations ".
Option 2
1. Give a definition of the terms:
A) polymer
B) heteropolymer
2. Which of the following are polymers?
A) glucose B) chitin
B) glycogen D) hemoglobin
3. Select monosaccharides from the following:
A) glucose E) sucrose
B) starch G) chitin
C) ribose H) lactose
D) glycogen I) fructose
E) deoxyribose K) cellulose
4.The composition of fats includes:
A) nucleotide
B) amino acid
C) glucose
D) glycerin
5. Substances that regulate the metabolism in the cell:
A) hormones
B) enzymes
B) vitamins
D) proteins
6. The sequence of monomers in a protein is called:
A) primary structure
B) secondary structure
B) tertiary structure
D) quaternary structure
7. Catalysts of chemical reactions are
B) carbohydrates
D) nucleic acids
8. Sign in front of the title organic matter numbers corresponding to the functions performed by the given substance in the cell.
Substances: Functions:
A) proteins 1.energy
2.structural
3.supply of nutrients
4.protective
5.information
6.catalytic
Test on topics: "Molecular and cellular levels"(Biology grade 9)
Choose one correct answer out of four.
A 1 ... After the appearance of the electron microscope, scientists discovered in the cell:
- nucleus 3) vacuole
- ribosomes 4) chloroplasts
A 2. In the table below, between the positions of the first and second column
there is a relationship.
Object Process
ribosome protein synthesis in the cells of the body
cell membrane…
In place of the pass in this table, you should enter:
1) synthesis of fats
2) transport of substances
3) synthesis of ATP
4) cell division
A 3. The hereditary apparatus of the cell is located in
1) core | |
2) ribosome | |
3) vacuoles | |
4) the Golgi apparatus A 4. The main result of photosynthesisis education:
A 5. You can tell a plant cell from an animal cell by:
A 6. The cellular structures formed by DNA and protein are called:
A 7. Protein in the cell is synthesized:
|
A 8. The digestion of food particles and the removal of dead cells occurs in the body with the help of:
- Golgi apparatus
- endoplasmic reticulum
- lysosomes
- ribosome
A 9. What is the function of the cell center
- participates in cell division
- participates in the synthesis of proteins
- participates in the transportation of organic substances
- participates in the breakdown of substances
A 10. What is the haploid set of chromosomes in cancer cells, if the diploid is 118:
- 236 2) 59 3) 100 4) 80
A 11. The set of chromosomes in an organism is called:
- Caries 2) karyoplasm 3) karyotype 4) genotype
A 12. The inner membrane of mitochondria forms:
- Grana 2) chromatin 3) cristae 4) stroma
A 13. An organoid that can reproduce on its own:
- EPS 2) mitochondria 3) nucleus 4) ribosome
A 14. Organic matter during photosynthesis is formed from:
- Proteins and carbohydrates
- Oxygen and carbon dioxide
- Carbon dioxide and water
- Oxygen and hydrogen
A 15. Membrane channels are formed by molecules:
- Proteins 2) carbohydrates 3) lipids 4) nucleic acids
IN 1. Establish a correspondence between the structure of the cell and its appearance. To do this, select a position from the second column for each element of the first column. Enter the numbers of the selected answers in the table.
Answer:
IN 2. Insert the missing terms from the provided list into the text.
Cellular organelles perform various functions that ensure the vital activity of the cell. So, for example, _______________ occurs in chloroplasts of plant cells, and ____________ is synthesized on ribosomes. In mitochondria, ____________ is produced and accumulated, and the nucleus stores __________.
- transport of substances 4-hereditary information
- photosynthesis 5-ATP
- starch 6- protein
AT 3. Choose three correct answers out of six.
Select the processes by which energy is stored in the cell:
- protein biosynthesis
- DNA doubling
- photosynthesis
- oxidation of nutrients
- oxygen-free breathing
- cell division
From 1. Read the text and fill in the table in accordance with its sections.
Protein biosynthesis
Protein biosynthesis is a process during which hereditary information encoded in genes is realized in the form of a specific sequence of amino acids in protein molecules. It all starts with the synthesis of messenger RNA in a specific area of DNA. Messenger RNA exits through the pores of the nuclear membrane into the cytoplasm and attaches to the ribosome. The cytoplasm contains Transport RNA and amino acids. Transport RNAs recognize at one end a triplet of nucleotides on messenger RNA, and at the other end they attach certain amino acids. Having attached an amino acid, the transport RNA goes to the ribosomes, where, having found the required triplet of nucleotides encoding this amino acid, it is cleaved into the synthesized protein chain. Each stage of biosynthesis is catalyzed by a specific enzyme and provided with the energy of ATP.
Answers:
Part A.
A10 | A11 | A12 |
Molecular level of organization of living nature. test grade 9 Ι option
1.The connection of two DNA strands into a spiral is carried out by bonds:
a) ionic
b) hydrogen
c) hydrophobic
d) electrostatic
2. Monosaccharides include:
a) lactose, glucose
b) deoxyribose, sucrose
c) glucose, fructose
d) glycogen, maltose
3. Polymers include:
a) starch, protein, cellulose
b) protein, glycogen, fat
c) cellulose, sucrose, starch
4. DNA and RNA monomers are:
a) nitrogenous bases
b) deoxyribose and ribose
d) nucleotides
5. The variable parts of the amino acid are:
a) amino group and carboxyl group
b) radical
c) carboxyl group
d) radical and carboxyl group
6. Which substance is highly soluble in water?
a) fiber b) protein c) glucose d) lipids
7. In what case is the DNA nucleotide composition indicated correctly?
a) ribose, phosphoric acid residue, thymine
b) phosphoric acid, uracil, deoxyribose
c) the remainder of phosphoric acid, deoxyribose, adenine
d) phosphoric acid, ribose, guanine
8. Amino acids in a protein molecule are linked by:
a) ionic bond
b) peptide bond
c) hydrogen bond
d) covalent bond
9. Enzymes are biocatalysts consisting of:
a) proteins b) nucleotides c) lipids d) fats
10. Carbon as an element is a part of:
a) proteins and carbohydrates
b) carbohydrates and lipids
c) carbohydrates and nucleic acids
d) all organic compounds of the cell
Molecular level of organization of living nature. test grade 9 ΙΙ option
1. What is the function of ribosomal RNA?
a) forms active centers of the ribosome
b) transfers information from DNA
c) transfers amino acids to ribosomes
d) all the listed functions
2. Molecules are built from amino acid residues:
a) carbohydrates b) proteins c) lipids d) fats
3. The secondary structure of the protein is maintained:
a) peptide bonds
b) hydrogen bonds
c) disulfide bonds
d) covalent bonds
4. In the process of biochemical reactions, enzymes:
a) accelerate reactions, but they themselves do not change
b) accelerate reactions and change as a result of the reaction
c) slow down reactions without changing
d) slow down reactions by changing
5. Which of the named chemical compounds is not biopolymer?
a) protein b) glucose c) deoxyribonucleic acid d) cellulose
6. Protein molecules differ from each other:
a) the sequence of alternating amino acids
b) the number of amino acids in the molecule
c) the form of the tertiary structure
d) all the specified features
7. Monomers of nucleic acids are:
a) deoxyribose and phosphate groups
b) ribose or deoxyribose
c) nitrogenous base, carbohydrate, phosphoric acid residue
d) nucleotides
8. What is the function of the transport RNA?
a) transfers amino acids to ribosomes
b) transfers information from DNA
c) forms ribosomes
d) all the listed functions
9. Polysaccharides include:
a) starch, ribose
b) glycogen, glucose
c) cellulose, starch
d) starch, sucrose
10. The cell contains DNA:
a) in the nucleus and mitochondria
b) in the nucleus, cytoplasm and various organelles
c) in the nucleus, mitochondria and cytoplasm
d) in the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids